This paper, which focuses on plasma technology and waste treatment, covers the field of environmental protection and a brief introduction to related ceramic materials.
With the growing population as well as the economic development makes the production of solid waste increase rapidly.
Therefore, how to deal with these wastes into useful materials is a major project in favor of human development.
Numerous researchers have devoted themselves to the in-depth study of environmentally friendly solid waste treatment technologies, and have developed a series of mature technological ideas, such as photochemical oxidation technology, pyrolysis technology and thermal plasma gasification technology, etc. Among them, thermal plasma can be used for the treatment of solid wastes. Among them, thermal plasma treatment of solid waste has the advantages of high temperature (103-104 K), high enthalpy, high reactivity, good controllability, etc., which opens up a new way for the harmlessness, minimization and resource treatment of solid waste.
Plasma is the fourth state of matter consisting of electrons, ions and neutral particles, and in the treatment of solid waste, the treatment of solid waste utilizes the properties of high temperature, high energy and high enthalpy of plasma. Plasma torch is one of the energy sources to make the waste gasification, the discharge between the electrodes will gas medium ionization, resulting in a high-temperature arc, high-temperature arc heating flow through the gaseous medium, thus generating a high temperature, ionization and conductivity of the plasma, the plasma flame temperature is generally in the 4,000-7,000 ℃, the highest up to tens of thousands of degrees, which for the pyrolysis of solid wastes into simple atoms This provides the energy required for the pyrolysis of solid waste into simple atoms. At high temperatures, the inorganic components of solid waste melt and solidify through rapid cooling to form glass, which can be used as building materials. The organic components are decomposed into syngas (the main components are CO and H2), which can be burned directly or used as a high-quality fuel and in the chemical synthesis industry. During the gasification process, the plasma heats up the syngas to a high temperature of 1200-1300 ℃, which can completely decompose the complex organic substances into small, simple molecules and avoid the production of toxic substances such as dioxins and furans. The production of toxic substances such as dioxins and furans is avoided.
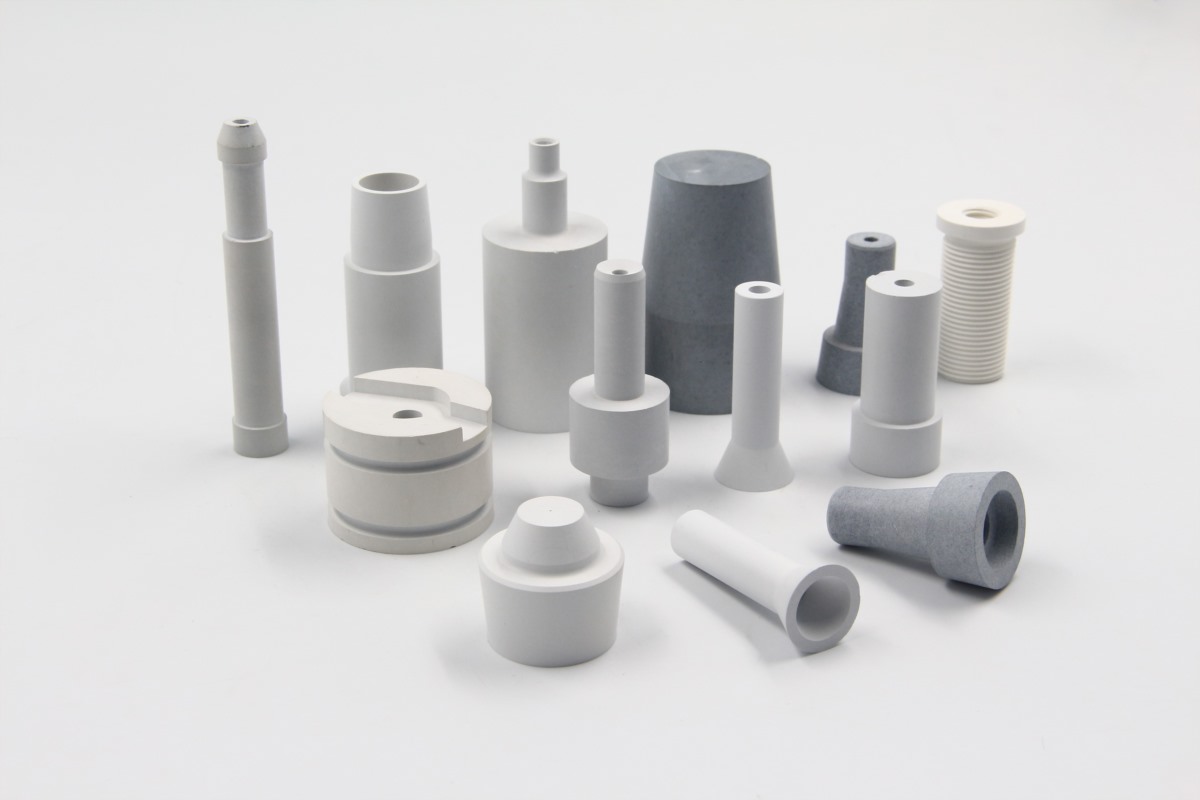
One of the ceramic materials involved is BN, which is resistant to high temperatures and corrosion, and is currently used in ultra-high-temperature plasma gasification technology, where BN is used in the plasma torch.

Involving the issue of technical confidentiality, this will not be elaborated in detail.
However, it can be seen that BN can be used in plasma technology, in the treatment of wastewater, waste and other environmental protection areas.
The following diagram shows the working principle of the plasma torch:
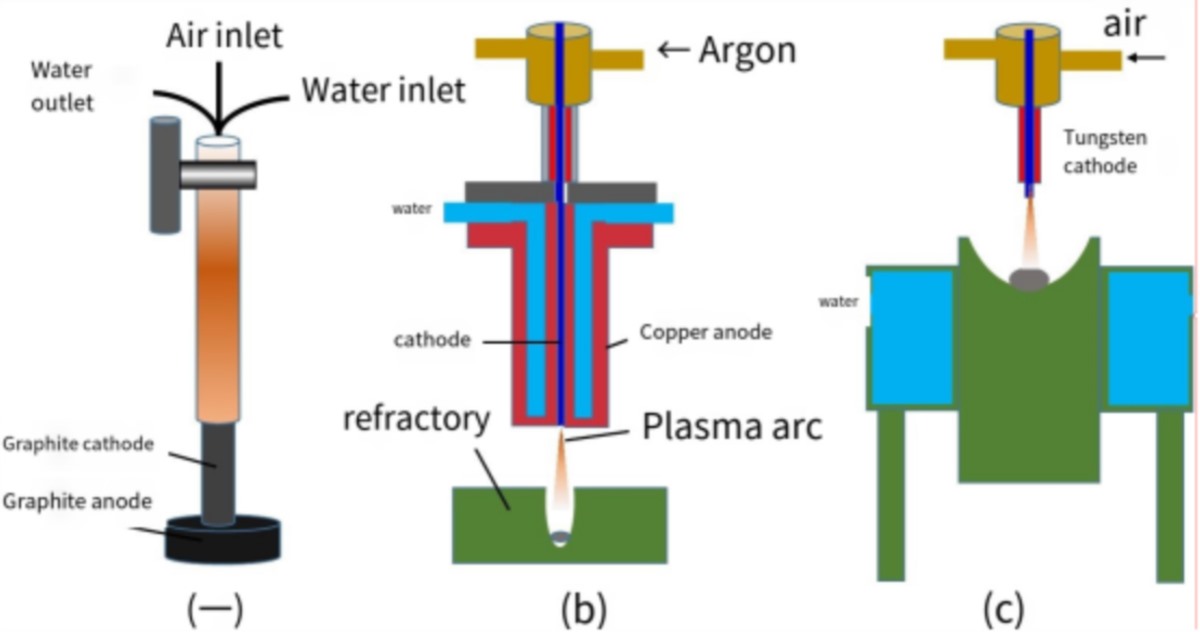
a)Low power transfer are plasma torch[; (b) non-transfer arc and (c) transfer arc plasma reactor
*Plasma technical analysis reprinted from 【ACTA PHYSICA SINIC】
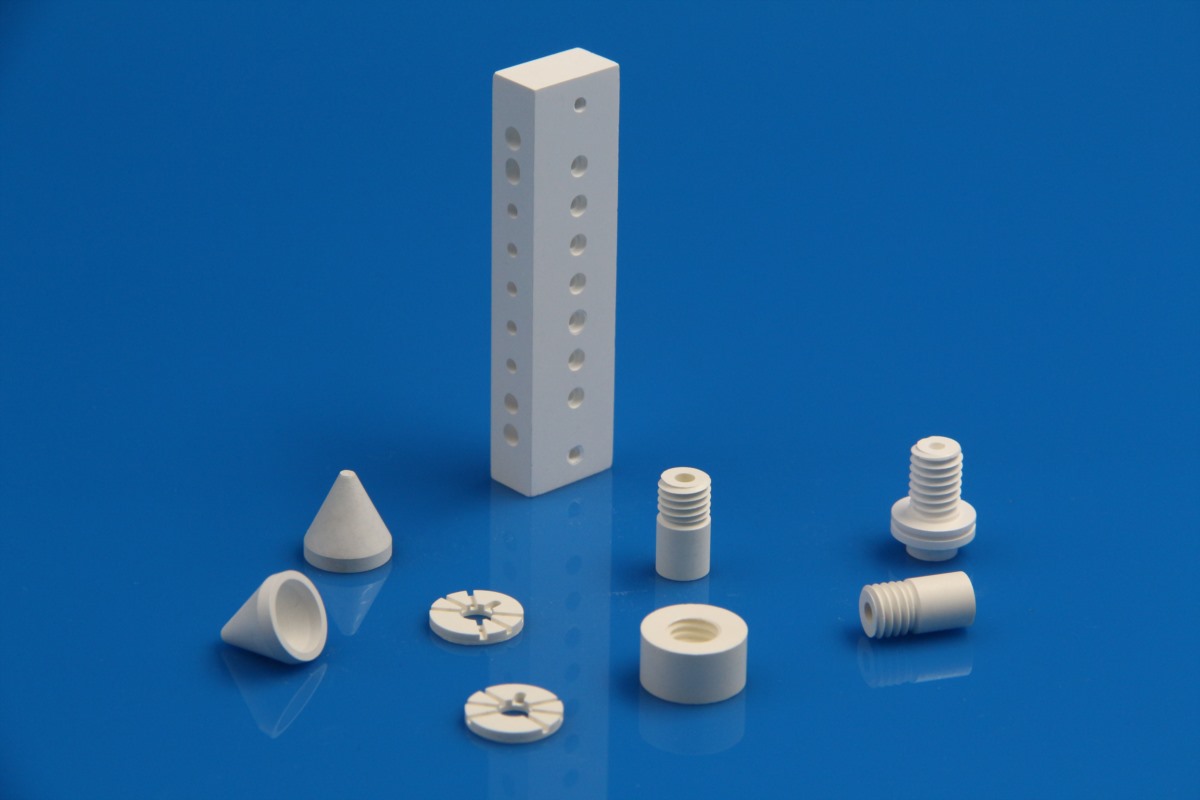
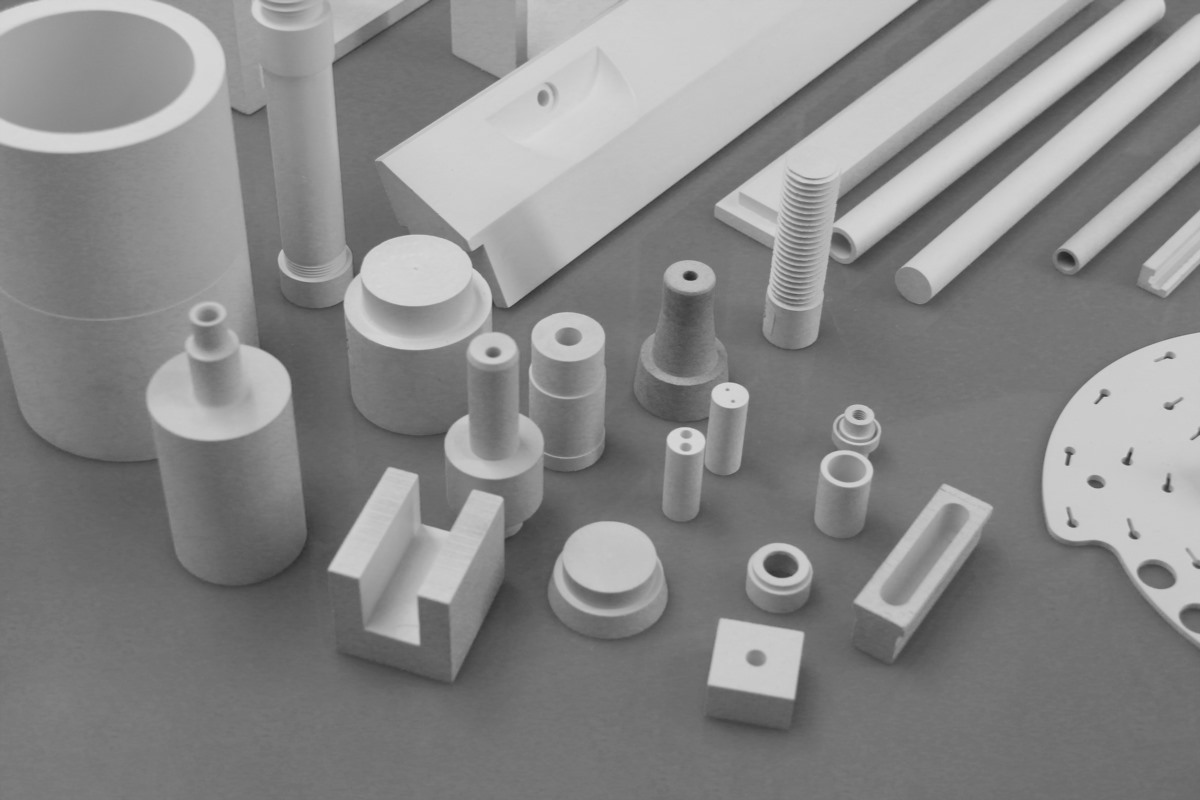
The following picture is for reference, welcome to customize.
Any more further detail, please contact:sales@innovacera.com.





 Enquiry
Enquiry