Introduction: What is an Oxygen Sensor?
An oxygen sensor is a key device for measuring the oxygen concentration in exhaust gas. At its core, the sensor relies on a zirconia or ceramic sensing element, supported by a built-in heater, which provides real-time feedback to the engine control unit (ECU). This feedback ensures that the engine maintains an ideal air-fuel ratio, thereby enhancing fuel efficiency, reducing emissions, and improving the overall performance of the engine.
Applications of Oxygen Sensors
Automotive
Installed both upstream and downstream of catalytic converters
Fundamental to meeting emission compliance standards (OBD-I and OBD-II)
Industrial
They are widely used in boilers, furnaces, and other combustion monitoring systems.
Environmental
Applied in gas detection, air quality monitoring, and safety systems
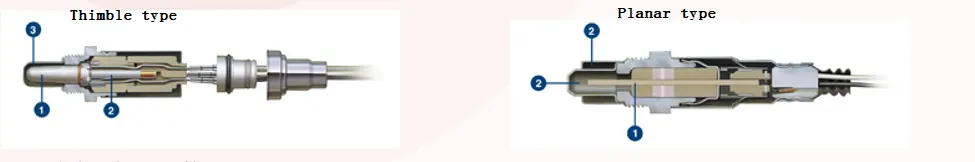
Types of Oxygen Sensors (Bosch Case Study)
Thimble Sensors: Traditional ceramic type, highly durable, requiring an external heater for fast activation.
Planar Sensors: Feature integrated heaters for quicker warm-up and lower power consumption.
Wideband / Air-Fuel Sensors: Measure precise oxygen concentration, allowing the ECU to fine-tune the air-fuel ratio.
Universal Sensors: Aftermarket-ready with flexible SmartLink™ connections.
The Role of Heaters in Oxygen Sensors
To ensure normal operation, the oxygen sensor must reach a working temperature of 300–400 °C. Without a heating device, the sensor can only rely on hot exhaust gases to warm up, which will delay its startup and result in higher emissions during cold starts. Integrated heating elements, such as ceramic heating chips, solve this problem. They can provide rapid and reliable heating at the moment of engine startup.

Market Trends
Increasingly strict emission regulations → more sensors per vehicle
Growing adoption of wideband sensors for hybrid and modern engines
Expand the replacement market (with a service life ranging from 30,000 to 100,000 miles)
The demand for cost-effective OEM and aftermarket solutions continues to grow.
Advantages of Heating Chips
Heating chips (ceramic heating elements) are becoming the preferred solution for oxygen sensors due to several advantages:
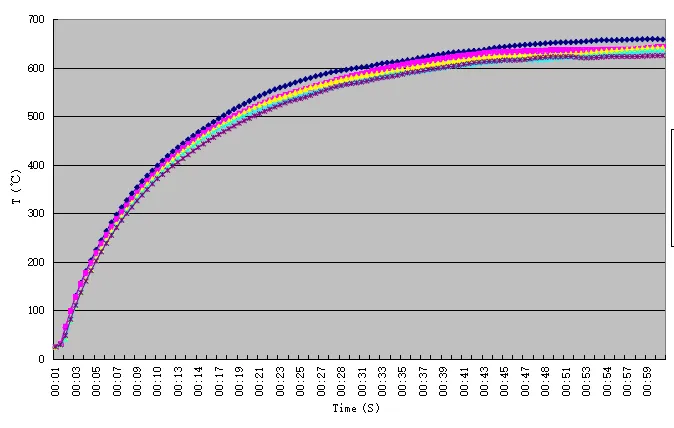
Cost Advantage: Significantly more cost-effective than traditional heating systems
High Performance: Rapid warm-up, stable operation, reduced cold-start emissions
Compact Design: Ideal for integration into planar and wideband sensors
Durability: Advanced ceramic materials ensure long service life
Our Advantages as a Supplier
Competitive Pricing: We deliver heater solutions with outstanding cost benefits.
Complete Component Supply: Beyond heating chips, we provide a full range of oxygen sensor parts.
Reliable Quality: Our products match OE standards and can be customized to customer requirements.
Oxygen sensors are indispensable in modern vehicles, industrial applications, and environmental monitoring systems. As the industry moves towards faster and more cost-effective heating solutions, ceramic heating chips will drive the next wave of widespread adoption in this field. With our highly competitive pricing, complete component supply, and excellent quality, we are fully capable of providing support to original equipment manufacturers and aftermarket partners, helping them meet future demands.
Declaration: This is an original article of INNOVACERA®. Please indicate the source link when reprinting: https://www.innovacera.com/news/oxygen-sensors-and-the-role-of-advanced-heating-elements.html.




 Enquiry
Enquiry