The use of Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramics
Basic information about Boron Nitride (BN)
Boron nitride (BN) is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory material, compound of boron and nitrogen. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal form corresponding to graphite is the most stable and soft among BN polymorphs. With excellent thermal and chemical stability, boron nitride ceramics are used in high-temperature equipment and metal casting, which has potential use in nanotechnology.
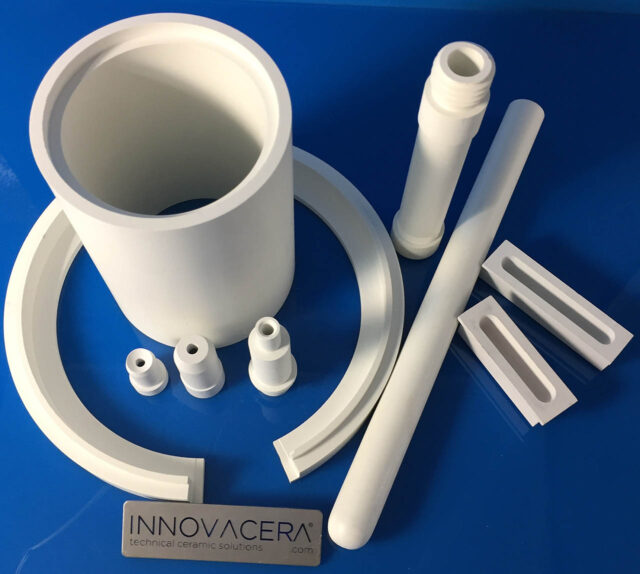

In the neutral reducing atmosphere, Boron Nitride’s heat resistance can be to 2000℃, the use temperature in nitrogen and argon can reach 2800℃, the stability is poor in the oxygen atmosphere below 1000℃. The expansion coefficient of hexagonal boron nitride is equivalent to that of quartz, but the thermal conductivity is ten times that of quartz.
Boron Nitride (BN) Material Available:
1. 99% BN
2. 99.7% BN
3. BN + AL
4. BN + Si
5. BN + SiC
6. BN + Zirconia
7. BN + ALN
The Following are the Characteristics of Different Boron Nitride (BN) Materials:
The Main Use of Boron Nitride Ceramics:
1. Vacuum high temperature equipment electrode insulation (99BN, BN+AL)
Advantage: high temperature resistance 2000 degrees, good thermal shock resistance, high electrical breakdown strength (3-4 times of alumina). Carbon atmosphere corrosion resistance is much stronger than alumina
2. Semiconductor equipment insulation heat dissipation (99BN, BN+ALN)
Advantages: large resistance, high temperature resistance, high breakdown resistance, no pollution corrosion resistance and processable
3. Gas atomizing nozzle (BN 99, BN+AL,BN+SIC,BN+ALN)
Mainly used in powder metallurgy industry, gas atomization process to produce metal powder (iron powder, aluminum powder, copper powder, stainless steel, welding powder, iron silicon aluminum, iron silicon nickel, aluminum iron boron, etc.)
Advantages: Resistance to metal corrosion wear and erosion, high thermal shock resistance, non-bonding and non-reaction with metal liquid.
4. Crucible for transparent ceramic sintering or bearing plate for Aluminum nitride, silicon nitride substrate (BN 99.7)
Advantages: high temperature resistance (2000 degrees), high purity (99.7% or more), no pollution of the product, no deformation at high temperature, and the product will not bond.












 Enquiry
Enquiry