Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Ceramic Substrates for Efficient IGBT Module Cooling
Behind the swift movement of electric vehicles, the operation of photovoltaic power stations, and the precise control of industrial production lines, there is a common core power component – the IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) module. It converts direct current into alternating current, precisely regulates the motor speed and torque, efficiently controls power switches, and completes the conversion and regulation of electrical energy. It is the “heart” of power electronic devices.
As the industry continuously enhances the performance and efficiency of systems, IGBT modules are evolving towards higher power density, smaller size, and greater reliability to meet the demands of lightweighting in electric vehicles, high power output, efficient operation of new energy inverters, as well as long lifespan and high reliability of industrial frequency conversion equipment. In such applications with high power and high heat load, safely and efficiently discharging the heat generated by the chip has become a major challenge in module design.
This answer is largely hidden within a seemingly insignificant component of the module – the base plate. It is not an ordinary metal plate, but a precise component made of a copper-ceramic-copper composite structure. The substrate of IGBT modules has traditionally been made of ceramic materials. For low-power modules, aluminum oxide, which is cost-effective and has mature manufacturing processes, is commonly used. However, in high-power and high-reliability applications, aluminum nitride has emerged as the key material for modern IGBT substrates due to its high thermal conductivity and excellent insulation properties.
Why aluminum nitride?
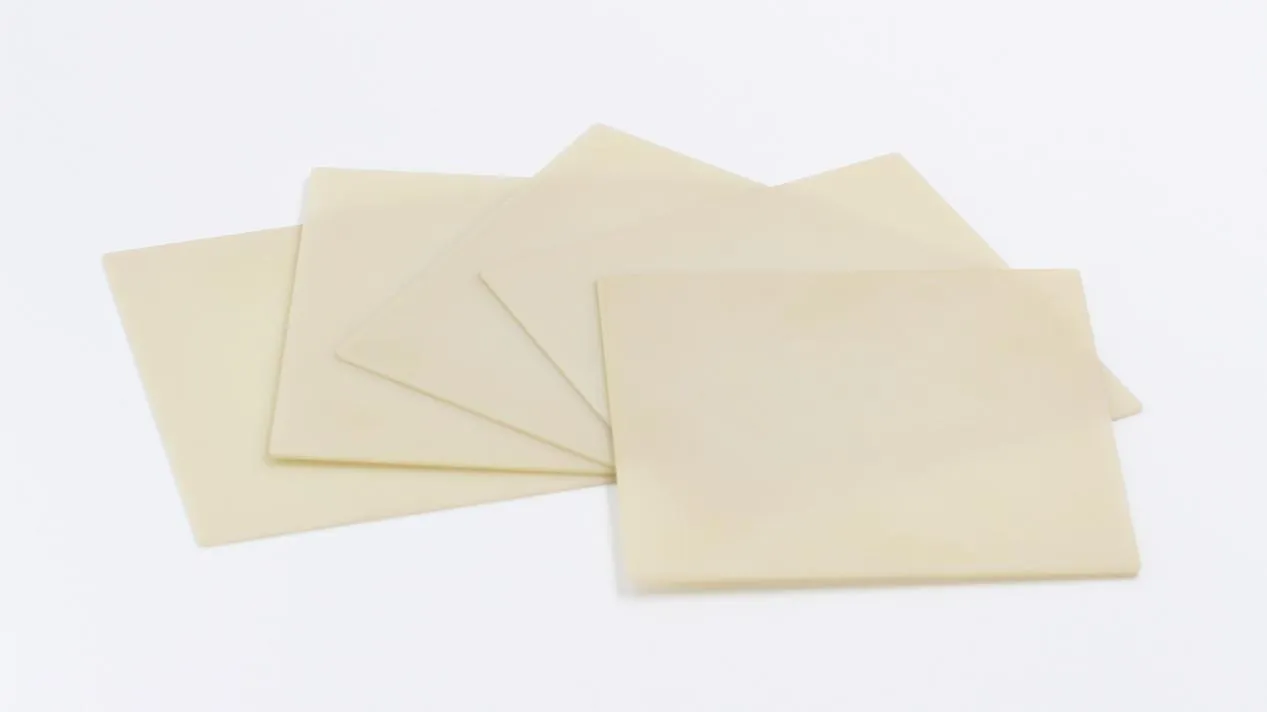

Aluminum nitride is an advanced functional ceramic. It is used in high-performance IGBT modules due to its outstanding physical properties:
(1) Excellent thermal conductivity: The thermal conductivity is as high as 170–230 W/mK, which is 6–8 times that of traditional alumina, enabling the rapid transfer of heat generated by the chip to the base plate, thus preventing overheating and failure.
(2) Reliable insulation: While achieving efficient heat conduction, AlN maintains a high volume resistivity and dielectric strength, enabling the construction of a stable electrical isolation barrier at the typical operating voltage of IGBT modules, ensuring operational safety.
(3) Matching thermal expansion: Its thermal expansion coefficient (~4.5×10-6/K) is close to that of silicon chips. During thermal cycling, it effectively reduces thermal stress and prevents the cracking of the soldering layer, thereby enhancing long-term reliability.
However, merely having high-performance ceramics is not sufficient to construct a complete module. It needs to be combined with metals in order to conduct current and dissipate heat.
DBC Technology: From Ceramics to Multi-functional Substrates
In order to fully utilize the material advantages of AlN, modern IGBT modules typically employ the Direct Bonded Copper (DBC) technology. This process achieves the bonding of high-purity copper foil firmly to both sides of the AlN ceramic sheet through a high-temperature eutectic reaction, forming a sandwich structure of copper-ceramic-copper. Each layer has a clear and coordinated function:
-Upper copper layer: As the circuit layer, it is used for soldering IGBT chips and conducting the main current.
-The middle AlN ceramic layer: It is the functional core, achieving both efficient insulation and rapid heat conduction.
-Lower copper layer: As a heat transfer layer, it conveys heat to the metal base plate and the external cooling system.
Through this structure, the AlN-DBC substrate is no longer an isolated ceramic, but becomes a multifunctional integrated carrier that integrates conductivity, insulation, heat conduction and mechanical support, laying a solid physical foundation for the high power density and high reliability operation of IGBT modules.
The core mission of AlN-DBC
In the IGBT module, AlN-DBC determines the performance limit of the module:
(1) Thermal Management
The high thermal conductivity enables the heat generated by the chip to be quickly dissipated, ensuring the stable operation of the module under high current and high power density conditions, and achieving miniaturization and high efficiency.
(2) Electrical insulation
Provide reliable insulation isolation between high-voltage chips and the grounding heat sink to ensure the safe operation of the high-voltage system (such as the automotive 800V platform).
(3) Mechanical Stability
The thermal expansion matching reduces thermal cycling stress, ensuring the interface reliability of the module during frequent start-stop, acceleration, and high-power cycles, significantly extending its service life.
For this reason, AlN-DBC has become the preferred solution for advanced applications such as electric vehicle main drive inverters, on-board chargers (OBC), high-power photovoltaic/storage converters, ultra-fast charging stations, and high-end industrial servo drives. It provides a solid material foundation for performance breakthroughs in these fields.
With the development of power electronics technology, IGBT modules are evolving towards higher power, smaller size and greater reliability. The AlN-DBC substrate provides crucial support for this trend and lays the foundation for future high-temperature applications of wide bandgap semiconductor devices. Innovacera can offer customized solutions for Aluminum nitride (AlN) Substrates, helping customers create high-performance and reliable next-generation power modules. Please feel free to contact us.

















 Enquiry
Enquiry