Porous Ceramics Applications: Atomizer Cartridges, Atomizing Core, Atomizer Core
Preface: atomization, the process of turning liquid into small droplets.
Nebulization products: humidifier, facial steamer, fog machine, medical nebulizer and so on.
With the development of science and technology, the atomization method is also diversified: high-pressure gas atomization, ultrasonic atomization, microwave heating atomization, resistance heating atomization.
As the Key of the atomization technology, the atomization core determines the atomization effect and experience.
Nowadays, ceramics in the field of fogging technology burst of vitality, become the standard of high-quality fog core.
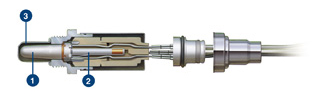
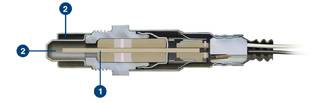
1. Why use ceramic as material and what is the principle of atomization?
Ceramic is not the only material applied to the atomizing core in electronic atomizers.
Fiber rope, organic cotton, non-woven fabric and other materials have been applied to make atomizing core.
The ceramic applied in the atomizer core is not the same as the ceramic we commonly see on the dining table, it is a special kind of “porous ceramic“.

This is a photo of the ceramic after magnifying it tens of thousands of times. In a ceramic core, there are about hundreds of millions of micro and nano pores like this one.

The main components of ceramic atomizer core are originated from nature, after high temperature sintering, a lot of tiny micro-pores are formed inside, and its average pore size is equivalent to one-fifth of a hair strand.
These tiny microporous holes are the key to the ceramic atomizer core’s ability to achieve stable liquid conduction and liquid locking functions. Due to surface tension and capillary effect, the liquid can penetrate into the atomizer core evenly and adsorb on the surface of the atomizer core.
2. What are the advantages of ceramic atomizer core?
Compared with the atomizing core composed of other materials, such as heating wire and fiber rope, heating wire and organic cotton, the Ceramic atomizing core is characterized by a faster rise in temperature during the heating process, better temperature uniformity and more precise control of the temperature range.
This can reduce the production of aldehydes and ketones in the process of use to a greater extent, thus ensuring the safety of the use process.












 Enquiry
Enquiry