What Are The Methods For Joining Ceramic With Other Metals
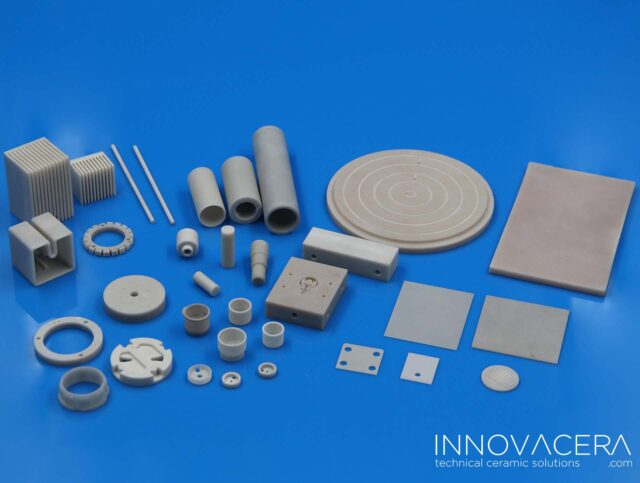
Joining ceramics to other materials, also known as ceramic-metal or ceramic-polymer joining, has been an area of extensive research and innovation. Engineers and scientists have been exploring various techniques to effectively bond ceramics, which are known for their high temperature resistance and hardness, with other materials like metals or polymers to create stronger and more versatile components.
Some of the common methods used for joining ceramics to other materials include:
1. Screwing: Used for junctions subject to strong impact such as in machine mechanisme.

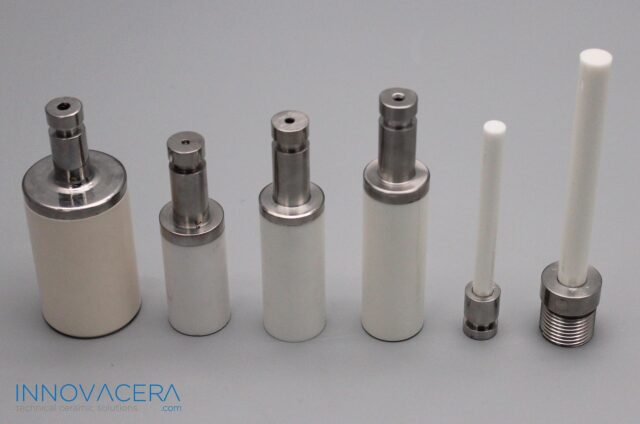
2. Shrink-fitting: Based on the higher compression resistance and lower thermal expansion of ceramics, it is used to reinforce ceramic pipes subject to internal pressure.

3. Resin molding: Ceramic parts are inserted and formed into desired shapes. Simple design is possible.

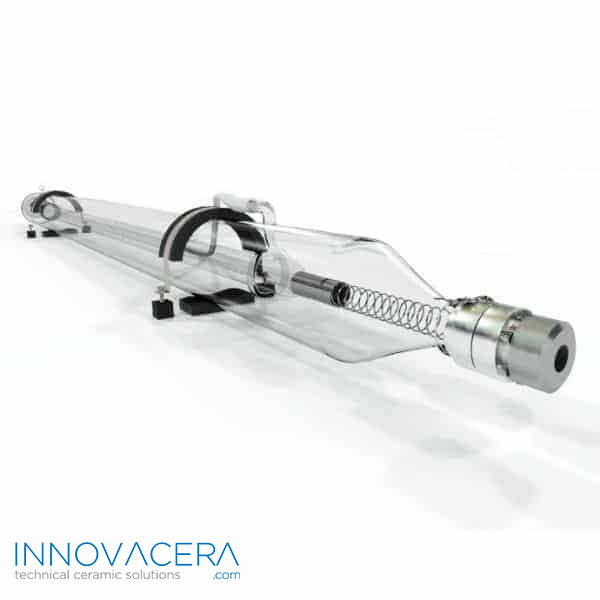
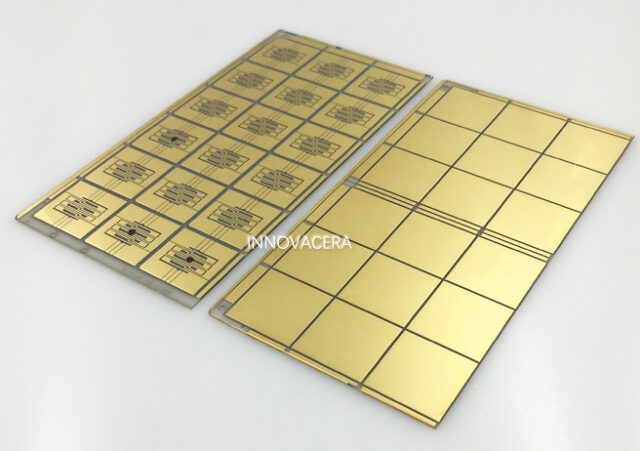
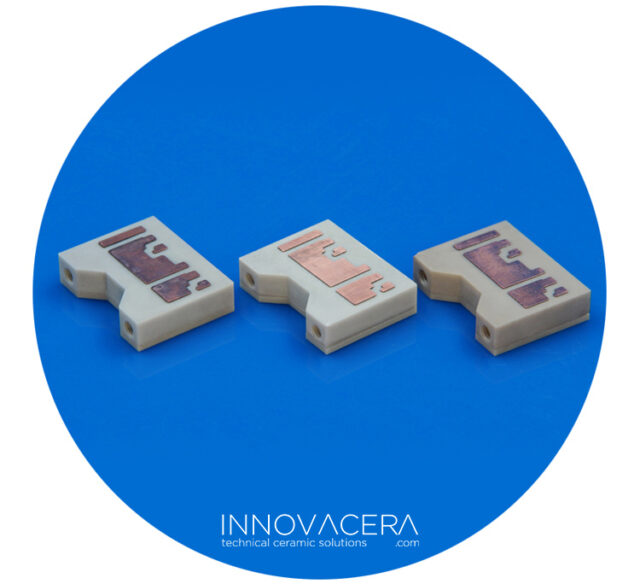
4. Brazing: A typical method used to seal ceramics and metal.Molybdenum-manganese paste is used as metal film is baked on the ceramics surface. The film formed is bonded to metal by high temperature brazing.

5. Adhesive Bonding: Using adhesives or bonding agents to attach ceramics to metals or polymers. Specialized adhesives are designed to withstand high temperatures and provide strong adhesion between dissimilar materials.

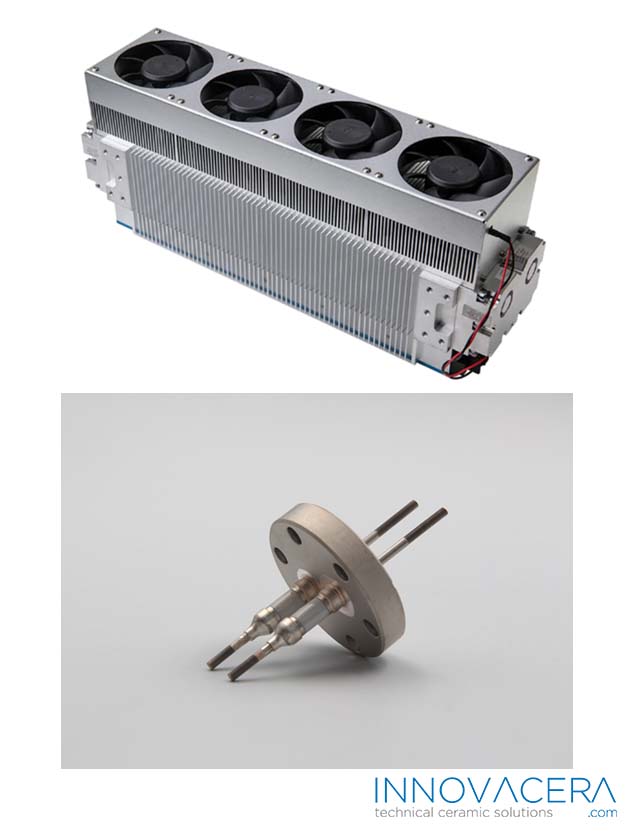
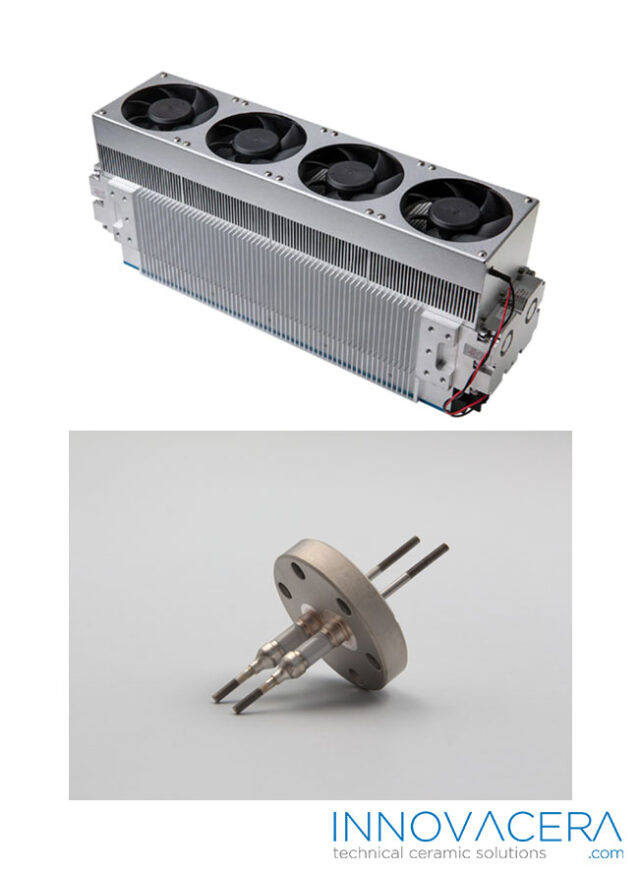
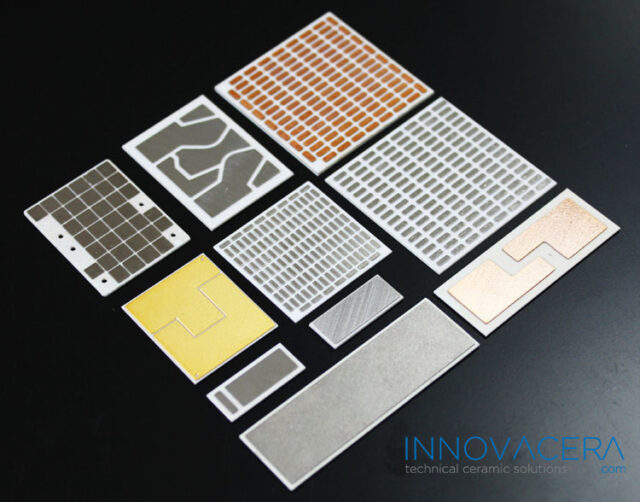
The successful joining of ceramics to other materials has numerous applications across industries. For instance, in aerospace, these techniques are used to create high-performance components that can withstand extreme conditions. In electronics, ceramics joined with metals enable the creation of advanced circuitry. Biomedical applications also benefit from such advancements, as they can create durable and biocompatible implants.
Recent advancements in material science and engineering have led to improvements in joining techniques, enabling stronger bonds and wider applications for ceramic-based materials in various industries.
At Innovacera, we can handle most ceramic joints. For more information on joining ceramic to other materials design and manufacture, please feel free to contact us directly.














 Enquiry
Enquiry