1. Application of silicon nitride ceramics in the mechanical field
Silicon nitride ceramics are used in the machinery industry as valves, pipes, classifying wheels, and ceramic cutting tools. The most common use is silicon nitride ceramic bearing balls.
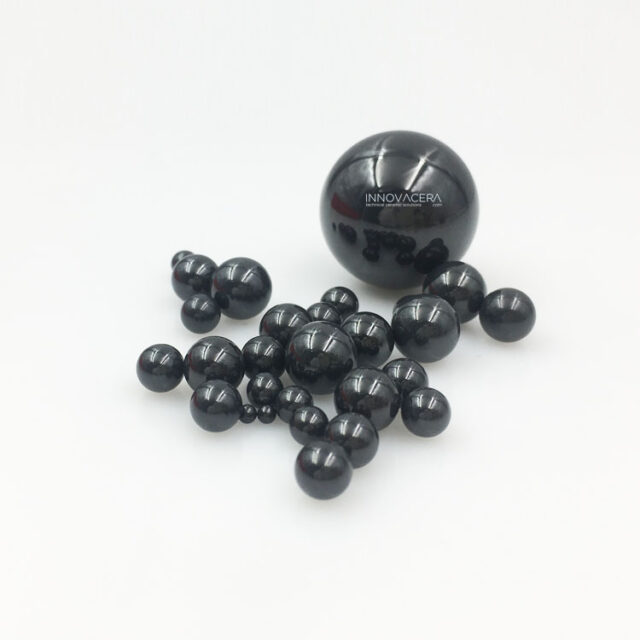

Compared with steel balls, silicon nitride ceramic bearing balls have outstanding advantages: low density, high temperature resistance, self-lubricating, and corrosion resistance. They are used in high-speed machine tool electric spindle high-speed bearings, aerospace engines, wind turbine bearings, and automobile engine bearings. Bearings for equipment such as
As a high-speed rotating body, the ceramic ball generates centrifugal stress, and the low density of silicon nitride reduces the centrifugal stress on the outer ring of the high-speed rotating body.
2. Application of silicon nitride ceramics in the semiconductor field
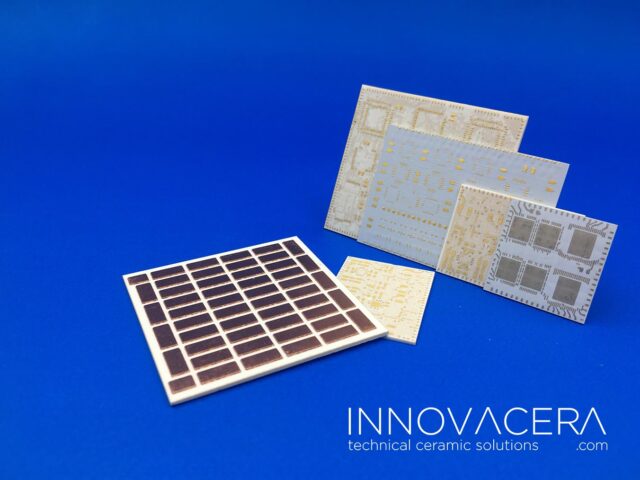
In addition to superior mechanical properties, silicon nitride ceramics also exhibit a range of excellent thermal conductivity properties, making them suitable for use in the demanding semiconductor field. In the field of integrated circuits, the degree of integration and power are increasing, which places higher requirements on the bending strength, stability, and heat dissipation capabilities of the substrates of packaged chips.

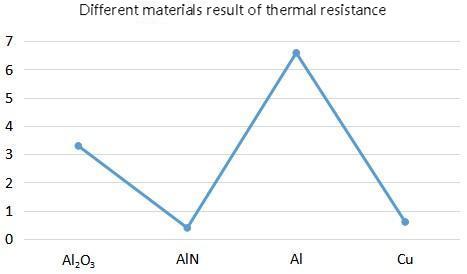
Silicon nitride ceramic substrates have higher thermal conductivity (typical values for commercial products are 80 to 90 W/mK). Compared with alumina substrates or ZTA substrates, they have more than three times the thermal conductivity and a thermal expansion coefficient (2.4 ppm/K) is small, close to semiconductor chips (Si, SiC), and has good thermal matching.
In addition, silicon nitride ceramic substrates have excellent mechanical properties, taking into account high bending strength and high fracture toughness. Compared with alumina substrates or aluminum nitride substrates, they have more than twice the bending strength, with a bending strength of 600 ~850MPa, fracture toughness is 5~7MPa·m½, so it has extremely high resistance to cold and thermal shock (extremely high reliability), and can weld very thick copper metal (thickness up to 800μm) to relatively thin nitride On silicon ceramics. Therefore, the current carrying capacity is high and the heat transfer is very good. Due to the excellent performance of silicon nitride substrates, it has good application prospects in power modules (IGBT/SiC power modules) for rail transit, wind power, photovoltaics, new energy vehicles, etc.
3. Application of silicon nitride ceramics in the field of bioceramics
As a new generation of bioceramic materials, silicon nitride ceramics not only have the excellent qualities that ceramic materials should have, but also have good radiographic properties, anti-infection properties, biocompatibility properties and osseointegration properties. They are widely used in biosensors, spine, and orthopedics. , dental and other implants are widely used.
4. Application of silicon nitride ceramics in the field of wave-transmitting materials
Silicon nitride ceramics and their composite materials have excellent properties such as heat resistance, wave transmission, and load-bearing, making them one of the new generation of high-performance wave-transparent materials studied. Due to the introduction of pores, porous silicon nitride ceramics have low density, low thermal conductivity, excellent pervaporation performance, and good transmittance of electromagnetic waves. In addition, they also have high specific strength, high specific modulus, high temperature resistance, oxidation resistance, and resistance to electromagnetic waves. Wear and other characteristics, it can be used as a ceramic-based wave-transmitting material to make radomes and antenna windows.











 Enquiry
Enquiry