Have you found an igniter you like?
INNOVACERA’s advanced igniters are simply the best for lighting wood pellet and biomass burners. They use only a fraction of the energy required by hot air fans and ignition blowers and will light all fuel types. Ideal for wood pellets, wood chips, lot, corn, maize, etc.
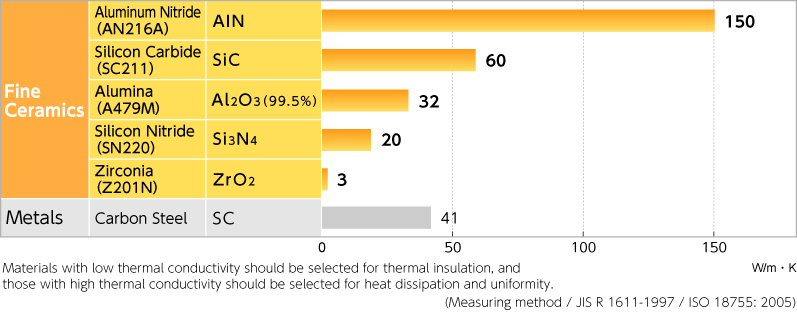
With a considerably higher temperature, around twice that of traditional metal sheathed products, ignition times are reduced to as little as 60 seconds. This makes them significantly more economical in use.
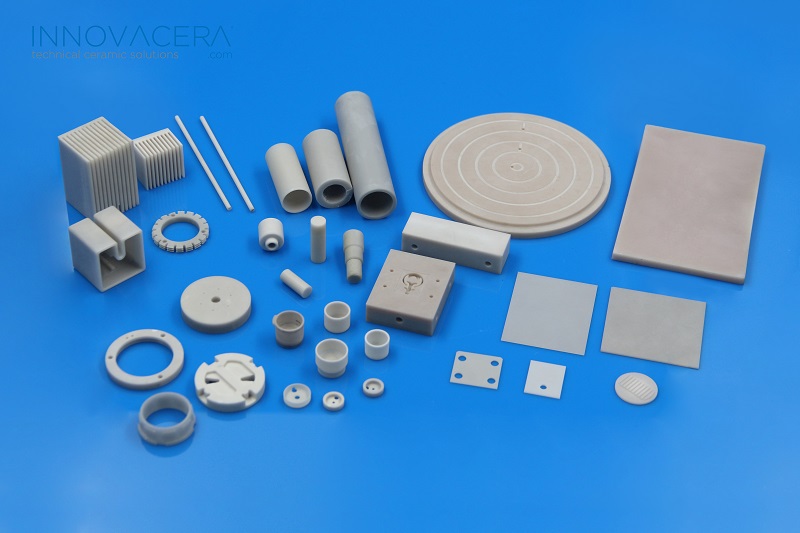
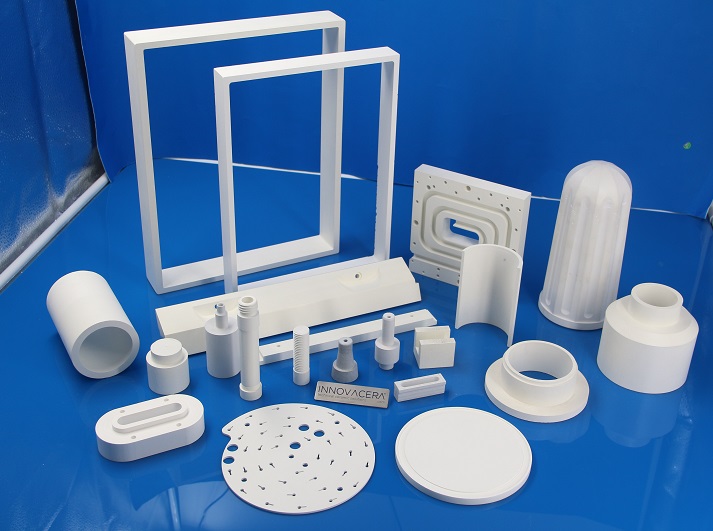
All our range can be customized to fit perfectly in your appliance
Further product advantages
• A fraction of the energy consumption compared to conventional heater
• Long lasting (non aging) • Time to ignition 60~90 seconds
• Easy to install and retrofit
• Fits any steel tube with an inner diameter of ≥18mm
• 1000°C at steady-state temperature
• Cannot overheat even with blower failure
• Available in 100V / 120V / 220V / 240VAC
• Fully electrically insulated with no exposed electric contacts
• Impervious to oxidation and corrosion
• Ignite wood pellet, wood chips, split logs, straw and other biomass
• Comply with RoHS, REACH regulation on Hazardous Subsctances
Application
•Wood pellet stove
• Wood pellet boiler
• Wood pellet burner
• Wood chips burner
• Straw burner
• Other biomass burner
Not without reason, the high temperature heating elements pellet igniter is the reliable standard ignition system for pellet heating systems in Europe-hundreds of satisfied customers speak for themselves.
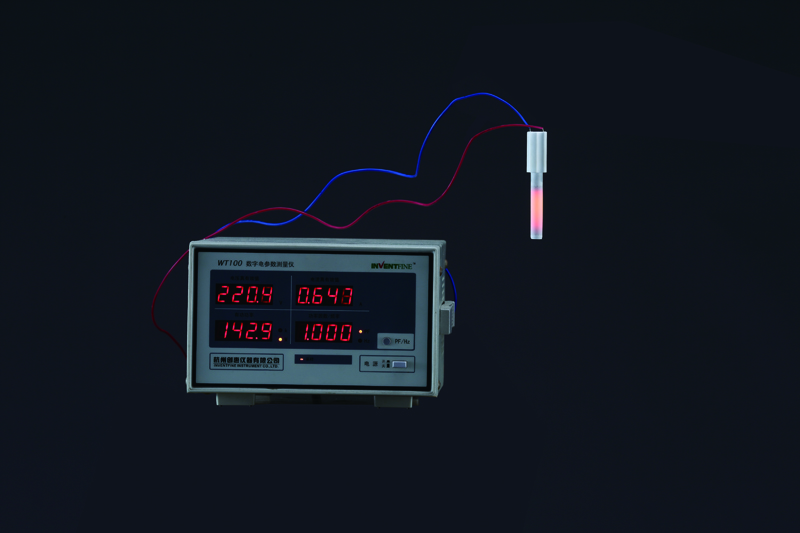
350W Alumina Ceramic Heater
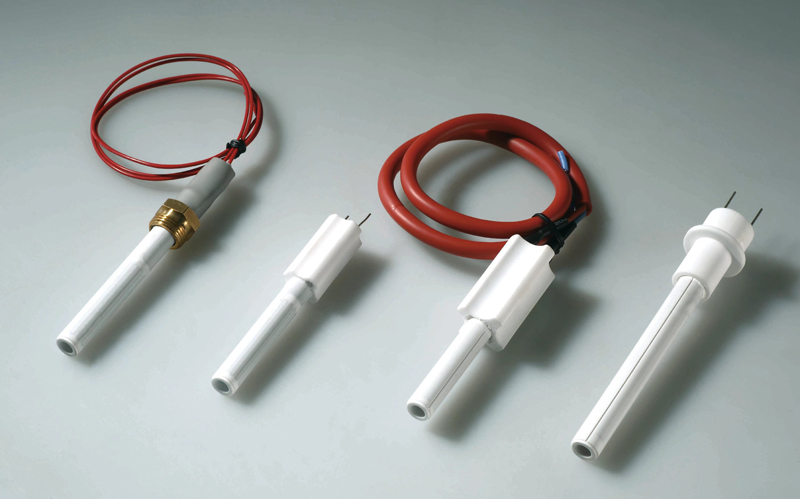

Alumina Ceramic Wood Pellet Igniter








 Enquiry
Enquiry