A brief introduction to HTCC
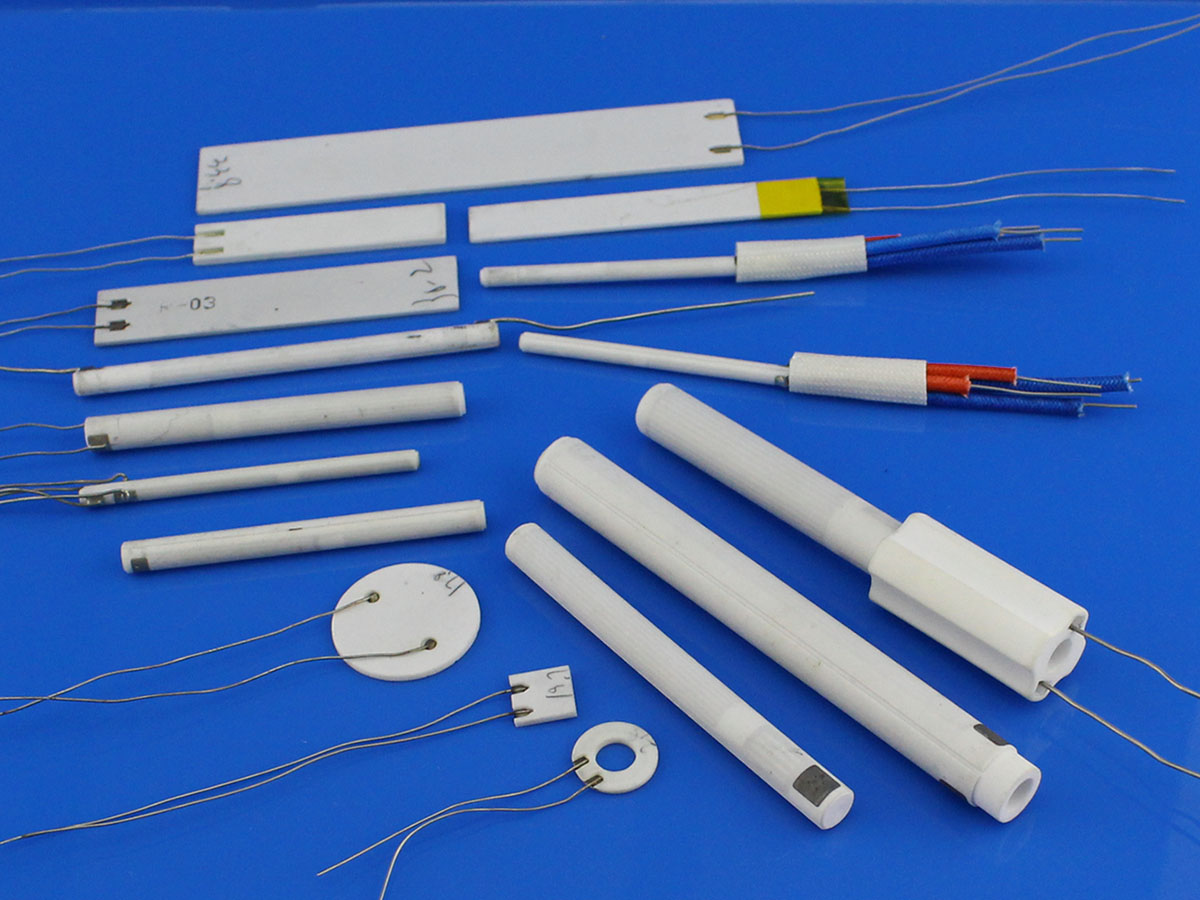
What is HTCC
HTCC (High Temperature co-fired Ceramic) adopts tungsten, molybdenum, molybdenum, manganese, and other High melting point metal heat resistance paste printed on 92 ~ 96% alumina flow Ceramic green billet according to the design requirements of heat circuit, 4 ~ 8% sintering agent and then laminated multilayer. In 1500 ~ 1600°C under high temperature burning into a whole.
Therefore, it has the advantages of corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, long life, high efficiency and energy saving, uniform temperature, good thermal conductivity, fast thermal compensation, and does not contain lead, cadmium, mercury, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyl, polybrominated diphenyl ethers, and other harmful substances, in line with the European Union RoHS environmental protection requirements.
Due to the high firing temperature, HTCC cannot use gold, silver, copper and other low melting point metal materials, must use tungsten, molybdenum, manganese, and other refractory metal materials, these materials have low conductivity and will cause signal delay and other defects, so it is not suitable for high-speed or high-frequency microassembly circuit substrate. However, HTCC substrate has the advantages of high structural strength, high thermal conductivity, good chemical stability, and high wiring density, so it has a wide application prospect in high-power microasse.
The classification of HTCC
In the high-temperature co-firing ceramics, alumina, mullite, and aluminum nitride are the most important components of ceramics.
1. Alumina
Alumina ceramic technology is a relatively mature microelectronics packaging technology, it is made of 92 ~ 96% aluminum oxide, adding 4 ~ 8% sintering additives at 1500-1700°C, its wire materials are tungsten, molybdenum, molybdenum – manganese and other refractory metals.
The substrate technology is mature, medium material cost is low, and thermal conductivity and bending strength are high. However, alumina multilayer ceramic substrate has the following disadvantages:
- High dielectric constant affects the improvement of signal transmission speed;
- High conductor resistivity and large signal transmission loss;
- The coefficient of thermal expansion is quite different from that of silicon, which limits its application in supercomputers.
2. Mullite
Mullite has a dielectric constant of 7.3-7.5, while alumina (96%) has a dielectric constant of 9.4, which is higher than mullite, so the signal transmission delay time of mullite is about 17% smaller than alumina. Moreover, the thermal expansion coefficient of mullite is very close to silicon, so this substrate material has been developed rapidly.
Mullite multilayer ceramic substrates have been developed by many companies and their products have good performance indicators. However, the substrate wiring conductor can only use tungsten, nickel, molybdenum, etc., and high resistivity and thermal conductivity are lower than alumina substrate.
3. Aluminum nitride
For aluminum nitride substrate, due to its high thermal conductivity, thermal expansion coefficient, and Si, SiC, and GaAs semiconductor materials match, its dielectric constant and dielectric loss are better than alumina, and AlN is a hard ceramic, can still work well under harsh environmental conditions.
For example, AlN ceramics still have excellent stability at high temperatures. Therefore, aluminum nitride as a multilayer substrate material has been widely studied at home and abroad and has made remarkable progress.
The disadvantages of aluminum nitride substrate are:
- Wiring conductor resistivity is high, signal transmission loss is large;
- High sintering temperature and large energy consumption;
- The dielectric constant is higher than that of low temperature co-fired ceramic dielectric materials;
- The thermal conductivity of aluminum nitride substrate decreases after co-firing with tungsten and molybdenum conductors;
- Screen printed resistors and other passive components can not be incorporated into the high temperature co-firing process because the metal oxides in the slurry of these passive components will react in the reducing atmosphere of the process and deteriorate the performance;
- The outer conductor must be nickel-plated and gold-plated to protect it from oxidation, increase the conductivity of the surface and provide a metalized layer that can be used for wire welding and tin welding component mounting.
In spite of these shortcomings, alN substrate has more advantages than other high temperature co-fired ceramic substrates in general, and has a good development prospect in the field of high temperature co-fired ceramics.
The application of HTCC
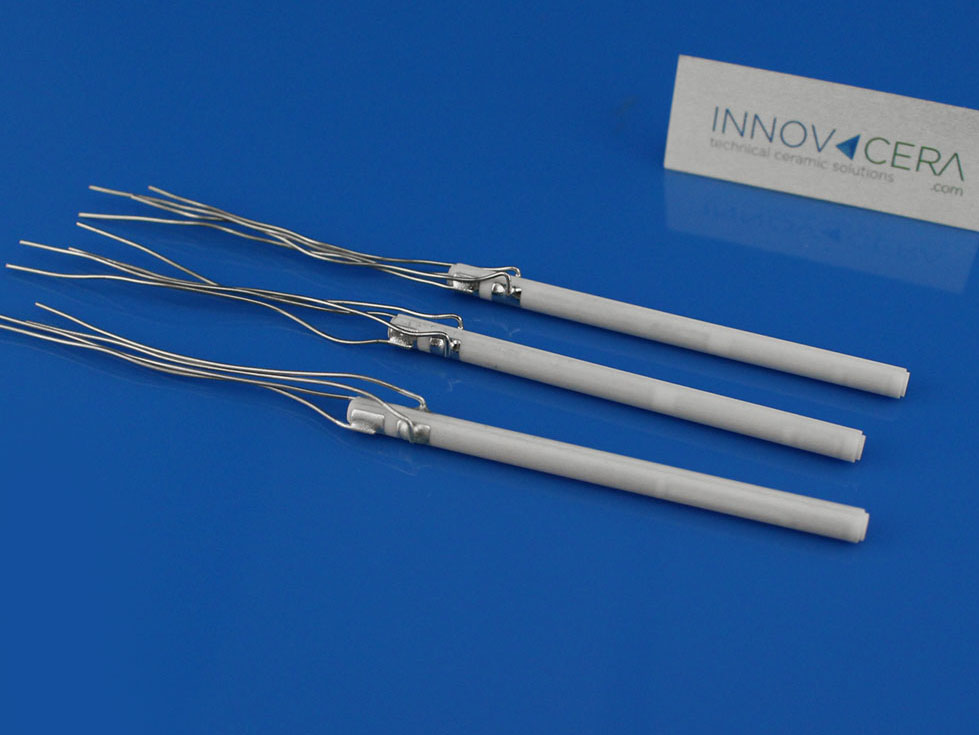
HTCC ceramic heating piece is a new type of efficient environmental protection and energy-saving ceramic heating element, compared with PTC ceramic heating element, with the same heating effect under the condition of saving 20 ~ 30% energy, so, the product is widely used in daily life, industrial and agricultural technology, military, science, communications, medical, environmental protection, aerospace, and many other fields.
Such as a small air heater, hair dryer, dryer, clothes dryer, heating machine, dehumidifier, hand warmer, dryer, electric splint, electric iron, electric iron, curling hair perm, electronic thermos flask, heat preservation box, heat preservation cabinet, kerosene carburetor, electric cooker, toilet ceramic heater, water heater, Infrared therapy instrument, intravenous injection heater, small special crystal device constant temperature tank, industrial drying equipment, electric adhesive, water, oil and acid, and alkali liquid heating elements.
INNOVACERA can customize ceramic heating elements according to demand, welcome to call or email for a consultation.


















 Enquiry
Enquiry