What Technology Enables Ceramics and Metals to Achieve A “Strong Combination”?
Ceramics are often referred to as inorganic non-metallic materials. It can be seen that people directly position ceramics on the opposite side of metal. After all, the performance of the two is worlds apart. But the advantages of the two are too prominent, so in many cases, it is necessary to combine ceramics and metals, each showing their strengths, so the technology-ceramic metalization technology was born.
Especially with the advent of the 5G era, the power of semiconductor chips continues to increase. The development trend of lightness and high integration is becoming more and more obvious, and the importance of heat dissipation is also becoming more and more prominent. This undoubtedly puts more stringent requirements on package heat dissipation materials. In the packaging structure of power electronic components, the packaging substrate serves as a key link for connecting the upper and lower parts and keeping the internal and external circuits connected and has functions such as heat dissipation and mechanical support. As an emerging electronic heat dissipation packaging material, ceramic has many advantages high thermal conductivity, insulation, heat resistance, strength, and thermal expansion coefficient matching the chip, so it is an ideal packaging heat dissipation material for power electronic components.
Ceramics used in circuits must first be metalized. A layer of a metal film should be applied to the surface of the ceramic. And to make it conductive, then welded with metal leads or other metal conductive layers. To be connected and become one.
The most important step in the ceramic-metal sealing process is metalization, and its quality affects the final sealing effect.
Difficulties in welding ceramics and metals:
1. The linear expansion coefficient of ceramics is small, while the linear expansion coefficient of metal is relatively large, causing the joints to crack. Generally, the thermal stress of the metal intermediate layer should be handled well.
2. The ceramic itself has low thermal conductivity and weak thermal shock resistance. When welding, it is important to minimize the temperature and control the cooling rate after welding.
3. Most ceramics have poor conductivity or even non-conductivity. It is difficult to use electric welding.
4. Due to the stable electronic coordination of ceramic materials, the connection between metal and ceramic is unlikely. Need to metalize ceramics or braze with active solder.
5. Since ceramic materials are mostly covalent crystals, they are not easily deformed, and brittle fractures often occur. At present, the intermediate layer is mostly used to reduce the welding temperature, and the indirect diffusion method is used for welding.
6. The structure design of ceramic and metal welding is different from ordinary welding. It is usually divided into flat seal structure, sleeve structure, pin seal structure, and double seal structure. The sleeve structure has the best effect, and the production requirements of these joint structures are very high.
The Mechanism of the Ceramic metalization
The mechanism of ceramic metalization is relatively complex, involving several chemical and physical reactions, the plastic flow of substances, and particle rearrangement. Various substances such as oxides and non-metal oxides in the metalized layer undergo different chemical reactions and substance diffusion and migration in different sintering stages. As the temperature rises, each substance reacts to form an intermediate compound, and when it reaches a common melting point, it forms a liquid phase. The liquid glass phase has a certain viscosity and at the same time produces plastic flow. After that, the particles are rearranged under the action of the capillary. Driven by energy, atoms or molecules undergo diffusion and migration, crystal grains grow, pores gradually shrink and disappear, and the metalization layer is densified.
The Process of Ceramic Metalization
1. Substrate pretreatment.
2. Preparation of metalization slurry.
3. Coating and drying.
4. Heat treatment.
The specific method of ceramic metalization
1. Mo-Mn method
2. Activation Mo-Mn method
3. Active metal brazing
4. Direct Bonded Copper (DBC)
5. Magnetron sputtering
Influencing factors of ceramic metalization
1. Metalization formula
2. Metalization temperature and holding time
3. Microstructure of metalization layer
4. Other factors













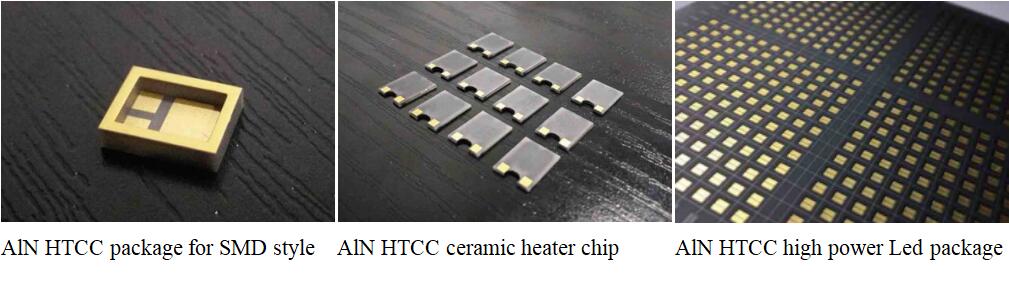
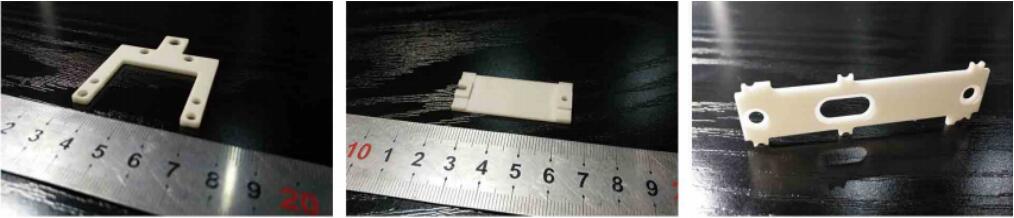
 Enquiry
Enquiry