Powder Injection Molding (PIM) is a component manufacturing process focused on forming complex-shaped, high-performance components in production quantities from metals and ceramics, metal injection molding(MIM) and ceramic injection molding(CIM). It is a combination of plastic molding and sintered powders technology.
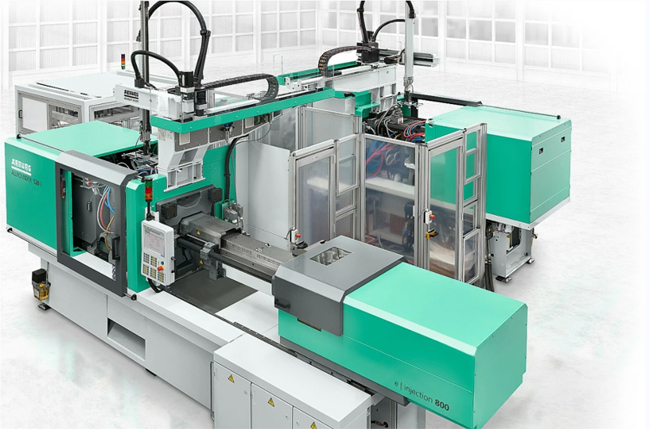

What is Metal injection molding(MIM)

Metal injection molding (MIM) merges two established technologies, plastic injection molding and powdered metallurgy.
This frees designers from the traditional constraints associated with trying to shape stainless steel, nickel iron, copper, titanium and other metals.
Most common engineering alloys are possible to produce by MIM, but about 30 alloys dominate the applications. The most popular alloys are surgical stainless steel (commonly called 17-4 PH, or American Iron and Steel Institute 630 or AISI 630) and austenitic stainless steels (AISI 304L and AISI 316L).
What is the process of Metal injection molding
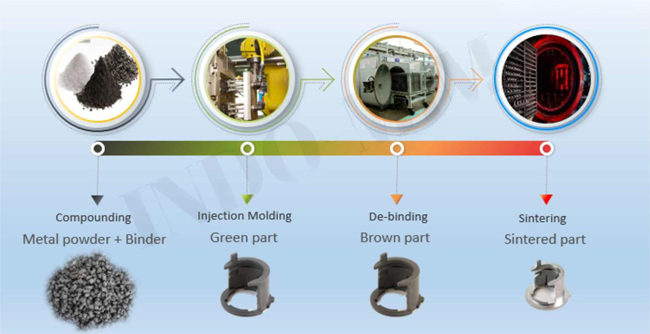
Step 1: Feedstock
Very fine metal powders are combined with thermoplastic and wax binders in a precise recipe. A proprietary compounding process creates a homogenous pelletized feedstock that can be injection molded just like plastic.
Step 2: Tooling
The tool cavity or mold for MIM is constructed as an enlargement of the final part. The space taken up by binder in the feedstock is annihilated by sintering. This is evident in that the final component is usually about 20% smaller than the tool cavity.
MIM tooling usually is hardened steel, such as S7 or H13. For lower volume or “bridge” tooling P20 can be used, when heat treated, this steel has some wear resistance. Harder tool steels are used for tooling for high production quantity situations.

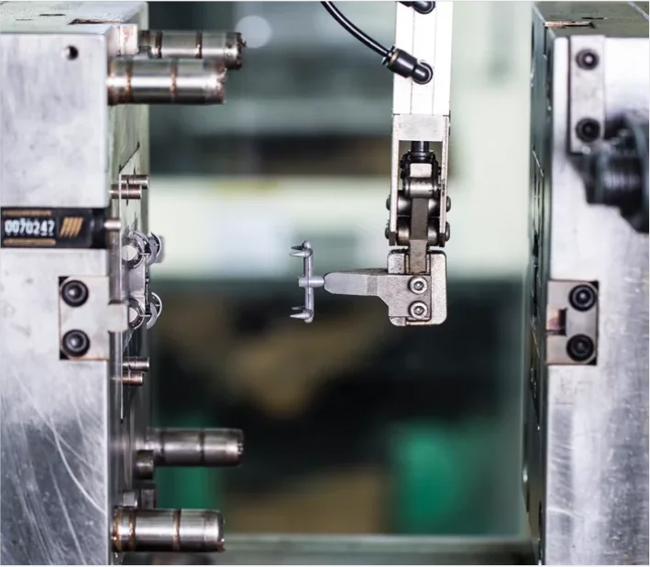
Step 3: Molding
The feedstock is heated and injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. This enables us to using like injection mold to produce extremely complex shapes.
After molded, the component is call “green” part. Its geometry is identical to the finished piece but is about 20% larger to allow for shrinkage during the final sintering phase.
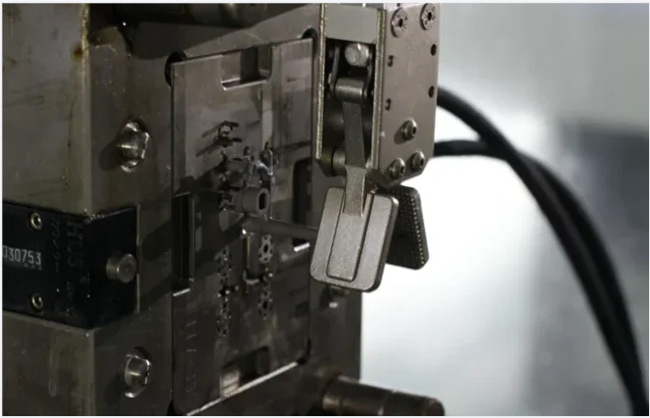

Step 4: Debinding
Binder removal (debinding) involves a controlled process to remove most of the binders and prepare the part for the final step – sintering.
Once debinding is complete, the component is referred to as “brown.”
Step 5: Sintering
The brown part is held together by a small amount of the binder, and is very fragile.
Sintering eliminates the remaining binder and gives the part its final geometry and mechanical strength.During sintering, the part is subjected to temperatures near the melting point of the material.

What is the key control point in sintering process

Control carbon potential is the key point in MIM sintering process, control carbon potential will improve the higher quality products and lowering the cost of production, enhancing customer satisfaction, and expanding the current and future market penetration of MIM.
The ceramic setter plate is the best choose in sintering process for Metal Injection Molding, there is there ceramic materials choose for MIM setter plate:
- Aluminum Oxide(Al2O3) ceramic setter plate: lower cost and its the most popular ceramic setter plate for Metal Injection Molding, max service temperature up to 1600°C(in air).
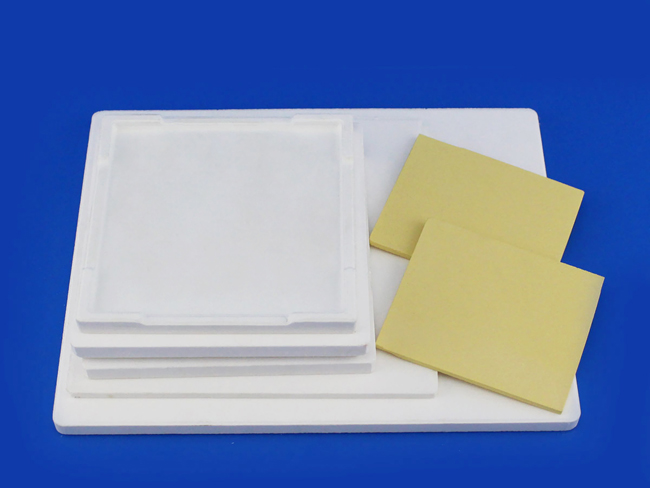

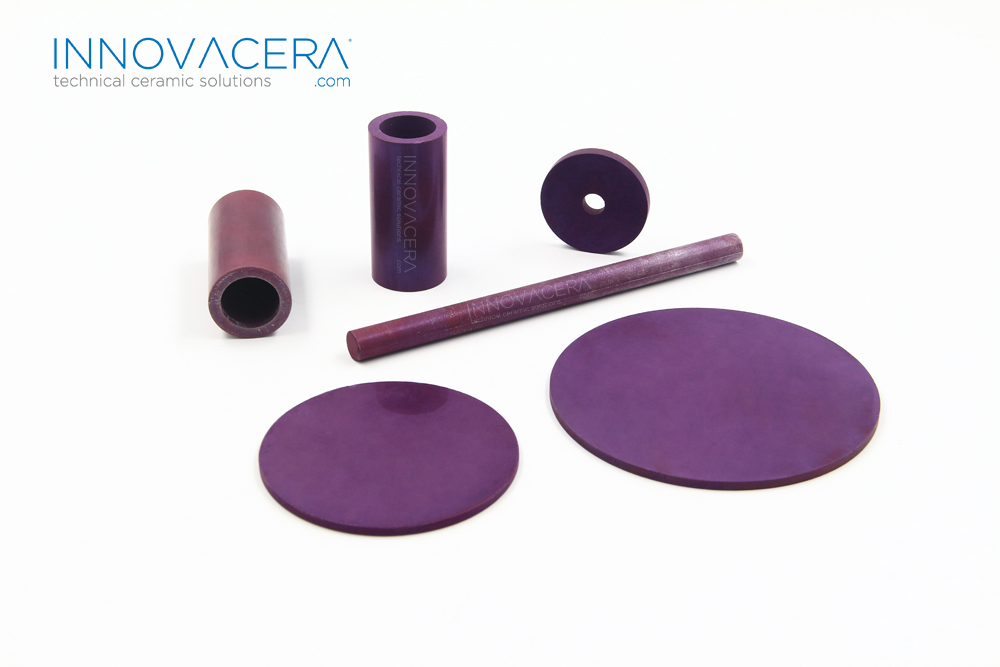
- Boron Nitride(HBN) ceramic setter plate:soft like graphite called “white graphite”, medium cost, long service life time, and used as setter plate for sintering high temperature up to 2100°C(Insert Gas).
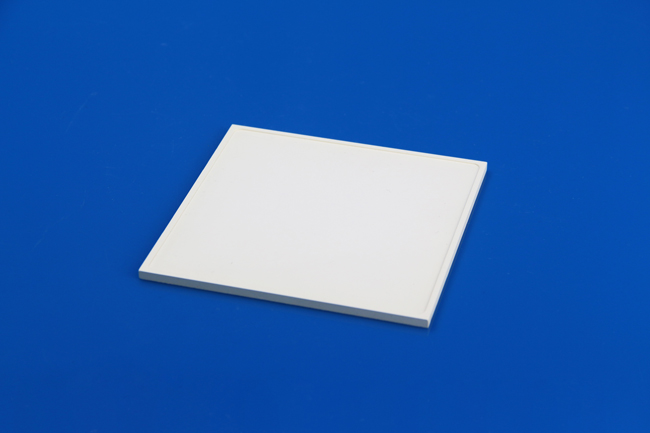

- Aluminum Nitride (AlN) ceramic setter plate: AlN ceramics is the basis for low lateral temperature differences and results in homogeneous thermal distribution within the sintering components.
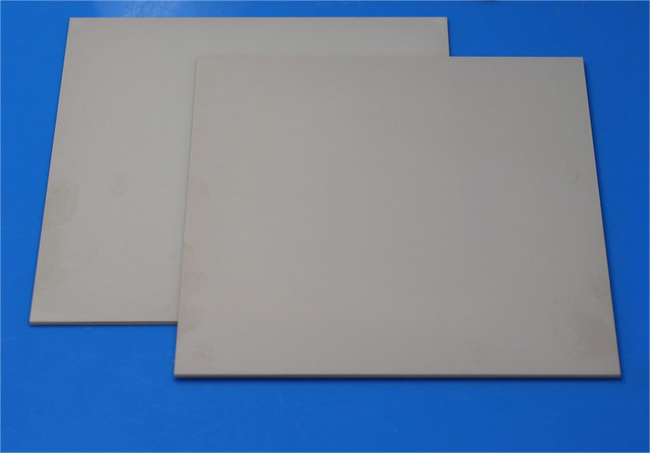

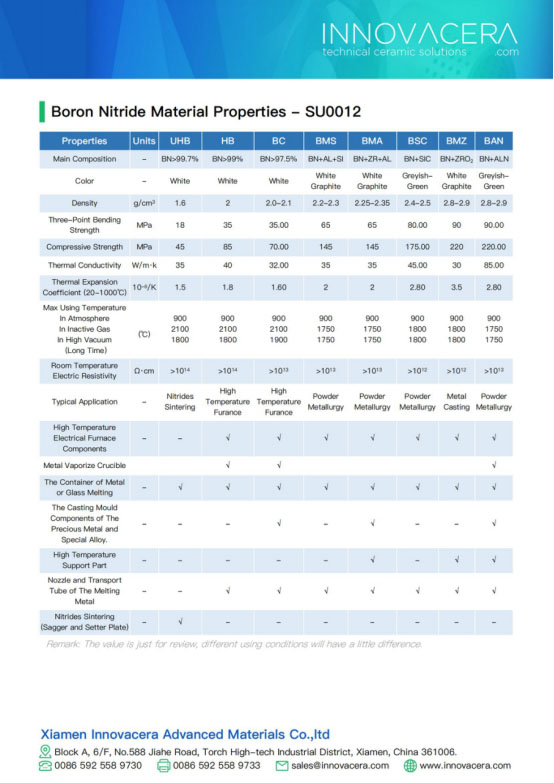
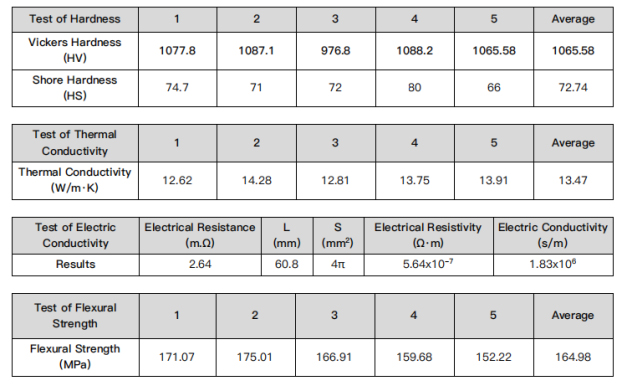
Ceramic Setter Plate Properties:
| Properties |
A-997
Aluminum Oxide |
HBN
Boron Nitride |
AN-170
Aluminum Nitride |
| Color |
Ivory |
White |
Dark Gray |
| Porosity Vol |
0~10% |
25% |
0 |
| Main Content |
99.7% |
99.7% |
95% |
| Bulk Density (g/cm3) |
3.9 |
1.6 |
3.3 |
| Bending Strength (MPa) |
320-340 |
18 |
382.7 |
| Coefficient Linear Thermal Expansion (X10-6/℃) |
7.6 |
1.5 |
2.805 |
| Max Using Temperature (℃) |
1600 |
2100 |
1850 |
As setter plates, alumina, boron nitride and aluminum nitride ceramics offer decisive advantages over conventional setters made from materials like graphite or tungsten. This enables energy and cost-efficient processing of high-precision sintering components.
Ceramic sintering tray and setter plates assist optimally array and fix molded parts in a sintering furnace to prevent brown part deformations during the firing process.
Roughness
Lower surface roughness ensures optimum gliding for molded parts. The smooth, particle-free surface also protects parts from contamination from the setters.
Thermal conductivity
High thermal conductivity of alumina ceramic, boron nitride and especially aluminum nitride ceramics is the basis for low lateral temperature differences and results in homogeneous thermal distribution within the sintering components. Excellent thermal shock resistance is another added benefit, which enables faster firing cycles.
High thermal resistance
This has a positive effect on the energy efficiency of the firing processes. Highly thermally resistant materials like advanced ceramics result in lower thicknesses of the setters, which improves energy efficiency because there is less thermal ballast. In addition, ceramic setter plates can also be used at temperatures far above 2100°C.
Inert surfaces
Advanced ceramics make using releasing agents or protective layers such as coatings obsolete, because there are no contact reactions with metals. Thus, these setter plates also have a long life time and do not require reconditioning. For example, molten metals cannot wet aluminum nitride ceramics. Aluminum nitride and ultrapure alumina (> 99%) can be used both in protective gas atmospheres and reduction atmospheres. They are also stable in reactive atmospheres and in hydrogen atmospheres.
High mechanical stability
This property, paired with low thermal capacity, not only results in a lower weight with a reduced tray volume; it also retains very little residual heat during the cooling process. This has a positive impact on energy consumption during firing.
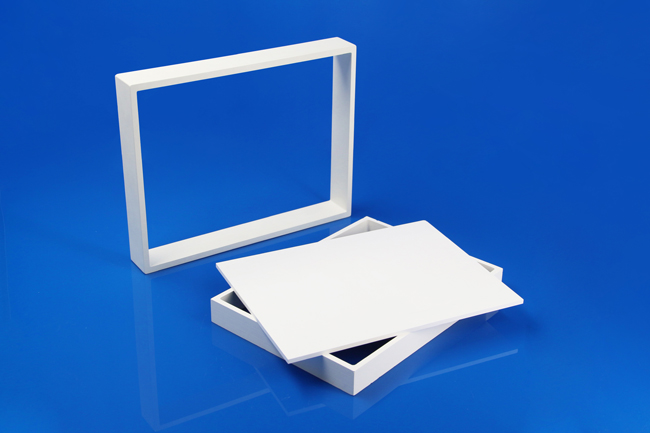

The maximum dimensions, such as 350 x 350 mm with HBN, enable a high packing density. These setter plates can be stacked – with integrated cavities on request – thereby ensuring fast, effective sintering furnace charging. This makes optimal use of furnace volume and energy expenditure, which results in a fully energetically optimized sintering process.
The ceramic setter plates can be used in ceramic injection molding (CIM), metal injection molding (MIM) and low temperature co-fired ceramics (LTCC). Recesses and customized designs are further cost-efficient options that are available on request.
If you have any question about the ceramic setter plates, welcome to contact us at sales@innovacera.com.





















 Enquiry
Enquiry