New functional ceramic materials are dielectric materials with electrical, magnetic, optical, acoustic, thermal, mechanical, chemical or biological functions. There are many types of functional ceramic materials and a wide range of uses, mainly including ferroelectric, piezoelectric, dielectric, pyroelectric New ceramic materials with different functions such as semiconductor, electro-optic and magnetic.

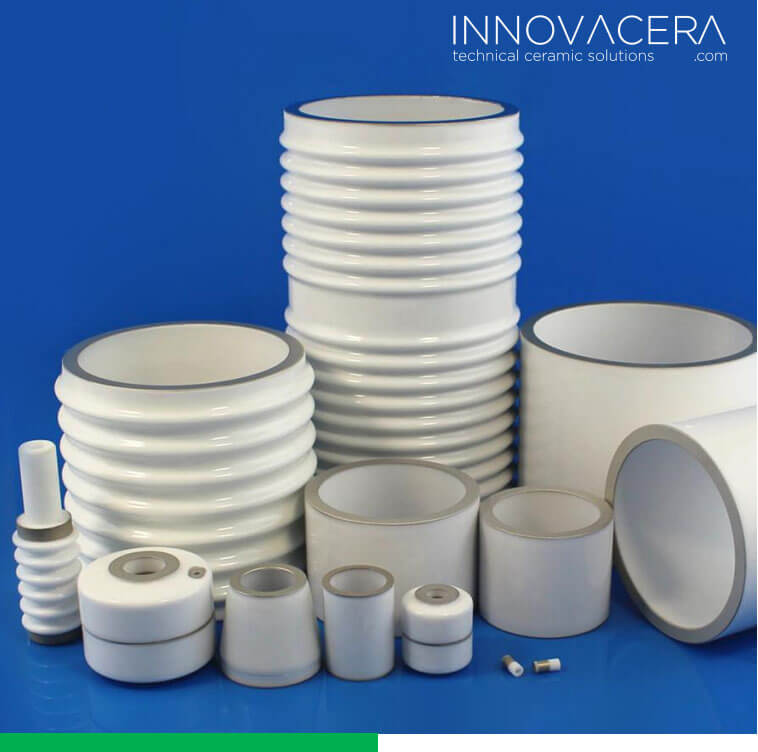
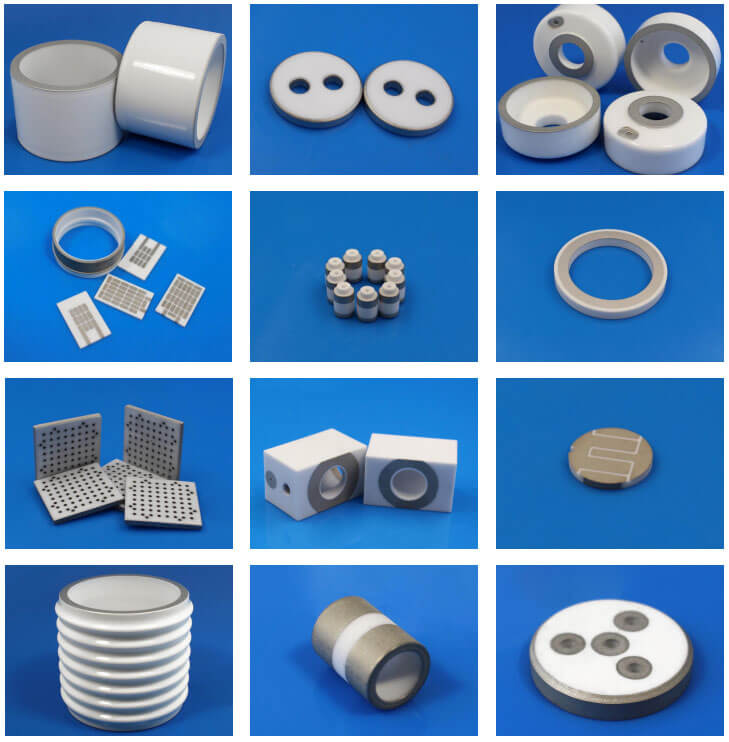
zirconia ceramics
New functional ceramic materials are important basic materials in modern high-tech fields such as electronic information, integrated circuits, mobile communications, energy technology, and national defense. Functional ceramics and their new electronic components play an important role in the development of the information industry and the enhancement of comprehensive national strength. strategic significance.
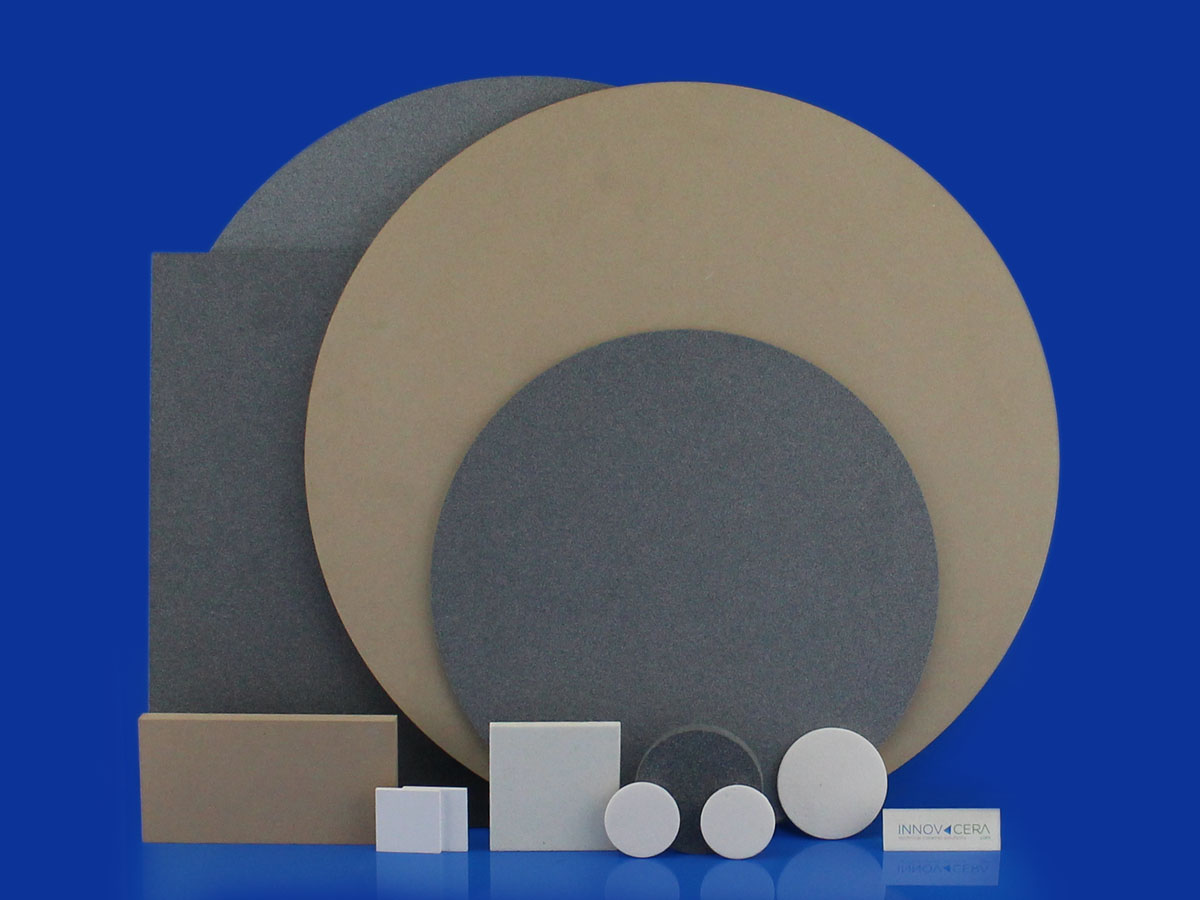
alumina porous ceramic
1.Semiconducting Ceramics
Semiconductor ceramics refer to polycrystalline ceramic materials formed by ceramic technology. Unlike polycrystalline semiconductors, semiconductor ceramics have a large number of grain boundaries, and the semiconductorization of grains is completed during the sintering process, so they have rich material microstructures. state and various process conditions, especially suitable for sensitive materials. In addition to semiconductor grain boundary ceramic capacitors, the sensitive materials currently used mainly include heat-sensitive materials, voltage-sensitive materials, photosensitive materials, gas-sensitive materials, moisture-sensitive materials, etc.
2.Magnetic ceramic material
Magnetic ceramics mainly refer to ferrite ceramics, which are composite oxides mainly composed of iron oxide and other iron or rare earth oxides. Ferrites are mostly semiconductors, and their resistivity is much higher than that of general metal magnetic materials. It has the advantage of small eddy current loss, and has been widely used in high-frequency and microwave technology fields, such as radar technology, communication technology, space technology, electronic computers, etc.
3.High temperature superconducting ceramics
High-temperature superconducting ceramics refer to functional ceramic materials that have a higher superconducting temperature than metals. Since the major breakthrough in the research of superconducting ceramics in the 1980s, the research and application of high-temperature superconducting ceramic materials have attracted much attention. In the past ten years, my country’s research in this area has been at the advanced level in the world. At present, the application of high-temperature superconducting materials is developing towards high-current applications, electronics applications, and diamagnetism.
4.insulating ceramic
Insulating ceramics refer to ceramic materials used in electronic equipment for installation, fixing, support, protection, insulation, isolation and connection of various radio components and devices. Insulating ceramics are required to have high volume resistivity, small dielectric coefficient, low loss factor, High dielectric strength, corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties.
Insulating ceramics are widely used in circuit substrates, packaging, high-frequency insulating porcelain and other industries. The main components include insulators, spark plugs, resistor base materials and integrated circuit substrates.
5.Dielectric Ceramics
Dielectric ceramics, also known as dielectric ceramics, refer to functional ceramics that have polarization ability under the action of an electric field and can establish an electric field in the body for a long time. Dielectric ceramics have high insulation resistance, high withstand voltage, small dielectric constant, dielectric Low loss, high mechanical strength and good chemical stability, mainly used in capacitors and microwave circuit components.
Dielectric ceramics include ceramic dielectric materials such as ferrodielectric ceramics, semiconductor dielectric ceramics, high-frequency dielectric ceramics, and microwave dielectric ceramics.
6.Nano functional ceramics
Nano-functional ceramics are new functional ceramics with antibacterial, activation, adsorption, and filtration functions used in air purification and water treatment. mineralization function.
7.Piezoelectric Ceramics
Piezoelectric ceramics refer to the ferroelectric ceramics which are formed by mixing oxides (zirconium oxide, lead oxide, titanium oxide, etc.) at high temperature and sintered at high temperature and reacted in solid state, and which have piezoelectric effect through direct current high voltage polarization treatment. The collective name of piezoelectric ceramics is a functional ceramic material that can convert mechanical energy and electrical energy. Due to its good mechanical properties and stable piezoelectric properties, piezoelectric ceramics are an important force, heat, electricity, and light-sensitive functional material. , has been widely used in sensors, ultrasonic transducers, micro-displacers and other electronic components.
Commonly used piezoelectric components include sensors, gas igniters, alarms, audio equipment, medical diagnostic equipment and communications, etc. The usual piezoelectric material is PZT, and the new piezoelectric ceramic materials mainly include: high-sensitivity, high-stability piezoelectric ceramic materials , electrostrictive ceramic materials, pyroelectric ceramic materials, etc.
8.Transparent functional ceramic
Transparent functional ceramic material is an optically transparent functional material. In addition to having all the basic characteristics of general ferroelectric ceramics, it also has excellent electro-optic effects. Through the control of components, it can present electrically controlled birefringence effects, electrically controlled light scattering Effect, electronically controlled surface distortion effect, electrostrictive effect, pyroelectric effect, photovoltaic effect and photostrictive effect, etc.

alumina-ceramic-components
Transparent ceramics can be made into electro-optic, electro-mechanical military and civilian devices for various purposes: optical switches for optical communications, optical attenuators, optical isolators, optical storage, displays, real-time display pagers, optical fiber docking Micro-displacement drivers, light intensity sensors, optical drivers, etc. used in optical fiber splicing and optical attenuators.

Boron-Nitride-Ceramic-Components
With the rapid development of material science, various new properties and new applications of functional ceramic materials are constantly being recognized by people. Functional ceramics have been widely used in energy development, space technology, electronic technology, sensing technology, laser technology, optoelectronic technology, infrared technology , biotechnology, environmental science and other fields are widely used. Functional ceramics are also developing in the direction of high performance, high reliability, multi-function, miniaturization and integration.













 Enquiry
Enquiry