Electronic ceramics market will reach 100 billion in 2022
Special ceramics have the advantages of high hardness, wear resistance, and high fracture toughness, the characteristics of ceramics and more than this, many ceramic materials also have extremely broad electrical characteristics, from insulators to semiconductors, conductors, and even superconductors are possible. Because of this, ceramic materials are widely used in the electronics industry.
The ceramic materials that can be used in electronic technology to prepare various electronic components are called “electronic ceramics”. Electronic ceramics also have the characteristics of high dielectric constant, low dielectric loss, small temperature coefficient, and so on, which can well meet the conditions of miniaturization and integration of the electronic industry. Therefore, electronic ceramics are very promising in the 5G era and are widely used in energy, household appliances, automobiles, and other aspects.
According to the data of relevant institutions, the market size of China’s electronic ceramics industry was 65.77 billion yuan in 2019, and CAGR reached 13.7% from 2014 to 2019. In the future, with the commercialization of 5G communications and the construction of data centers, the demand for electronic components, new energy fuels, and other fields increases, and the superposition of the domestic substitution trend of electronic ceramics, it is expected that the market size of China’s electronic ceramics industry will continue to maintain a rapid growth trend, and is expected to exceed 114.5 billion yuan in 2022.
Electronic ceramics refers to the use of electrical and magnetic ceramics in the electronics industry. The upstream of the electronic ceramics industry includes electronic ceramics base powder, formula powder, metal materials, chemical materials, etc. The middle reaches are electronic ceramic equipment and electronic ceramic materials. The downstream of electronic ceramics are mainly electronic components, which are eventually applied in terminal products. Its application fields are very broad, including optical communication, wireless communications, industrial laser, consumer electronics, automotive electronics, etc., and it is mainly used in the oscillating, coupling, filtering, and other circuits in all kinds of electronic whole machines.
Under the background of strong support of industrial policies, China’s electronic ceramics industry has developed rapidly, and the technical level of some electronic ceramic shell products has reached or approached the international advanced level, and the market share of Chinese manufacturers will be further expanded in the future.

Electronic ceramics market will reach 100 billion in 2022

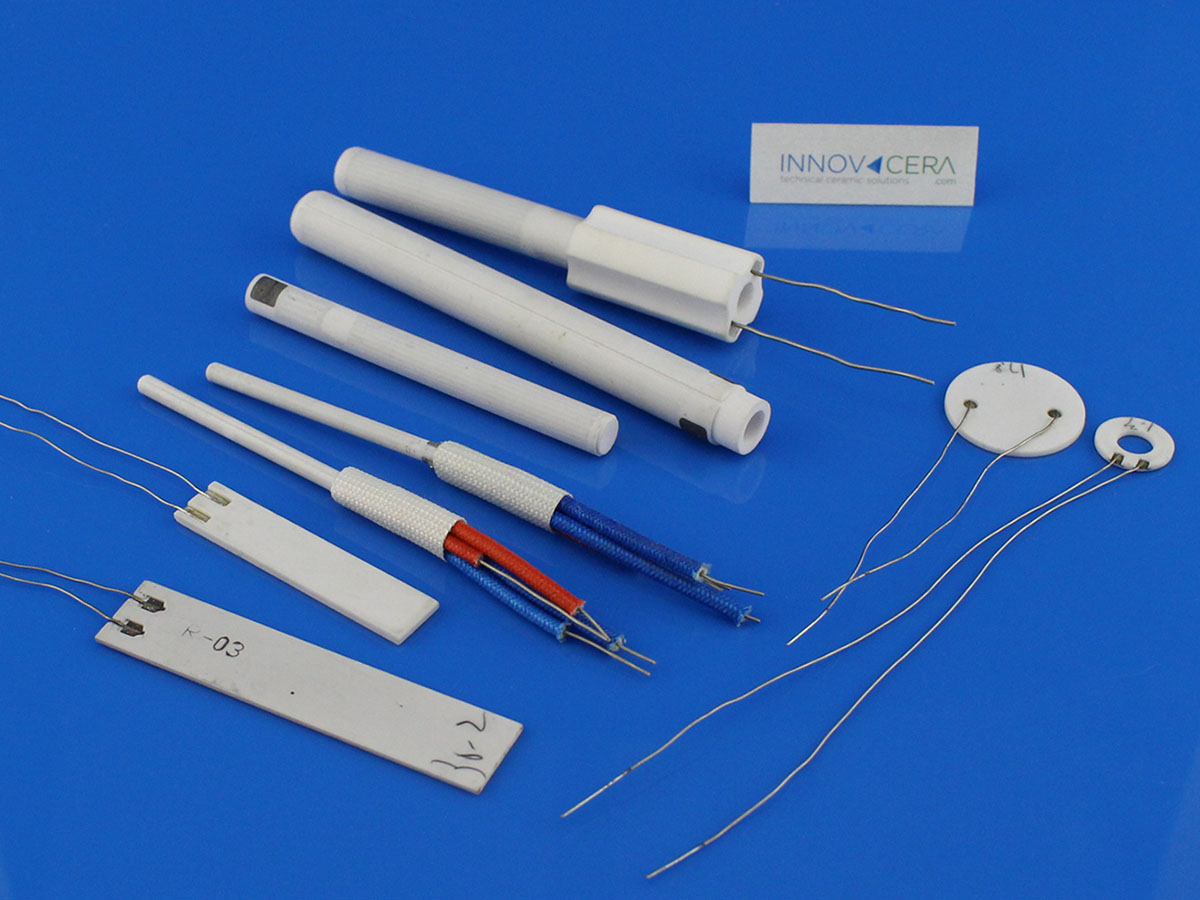





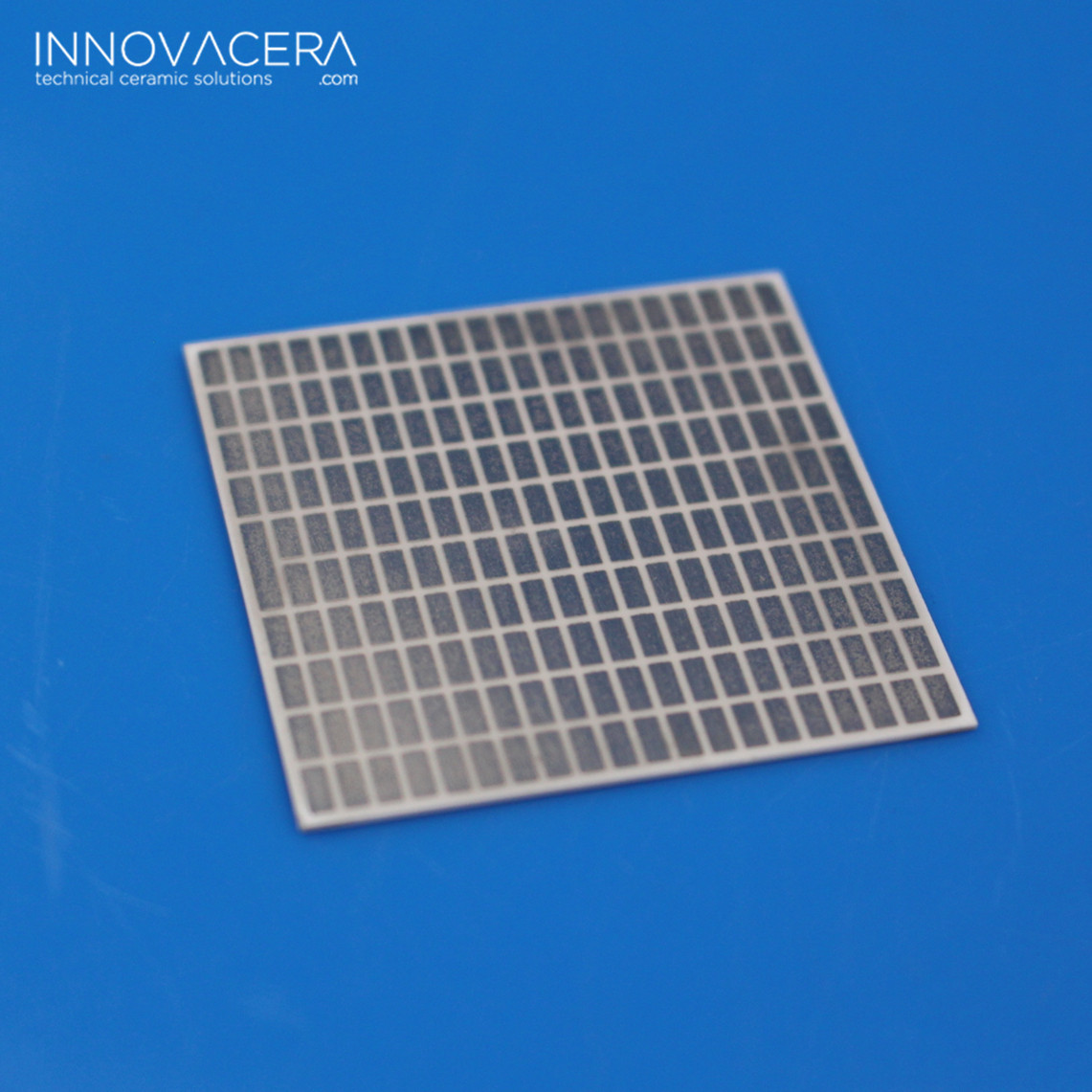


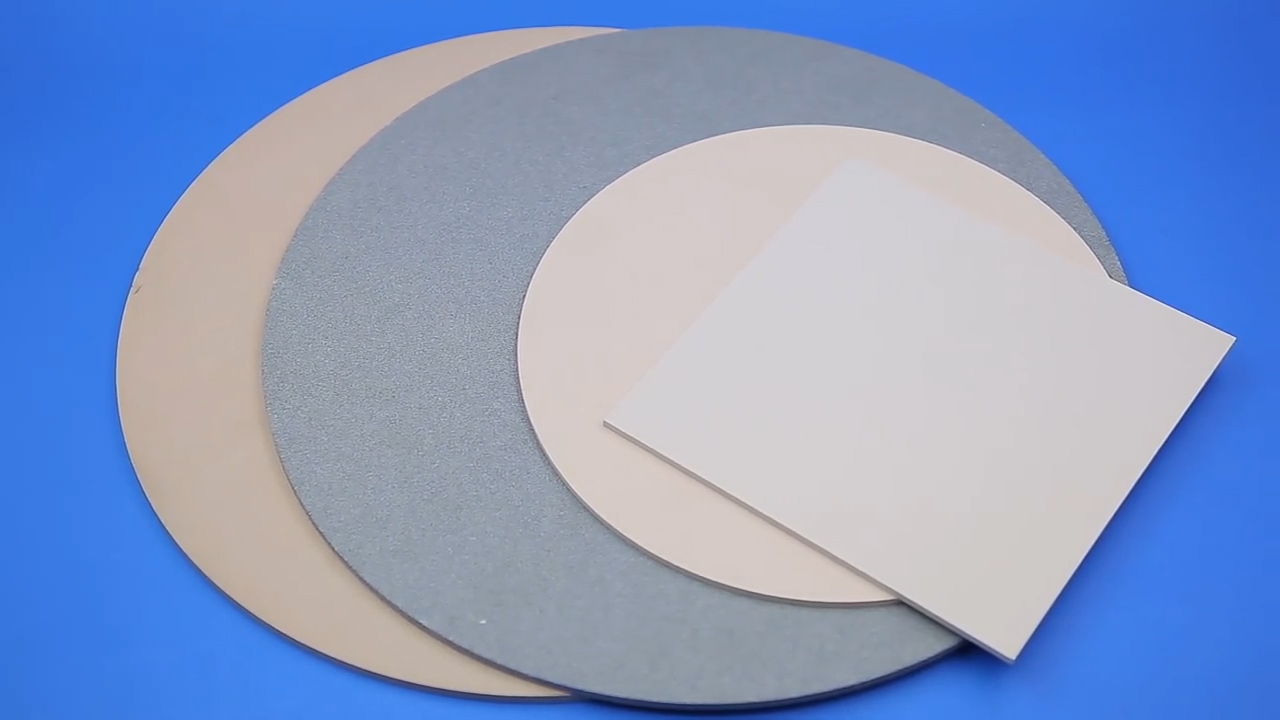

 Enquiry
Enquiry