How are advanced ceramic components made?

Advanced technical ceramics are generally produced on a relatively small scale. Expensive raw materials are used, but these are compensated for with the resultant improved properties and consistency.
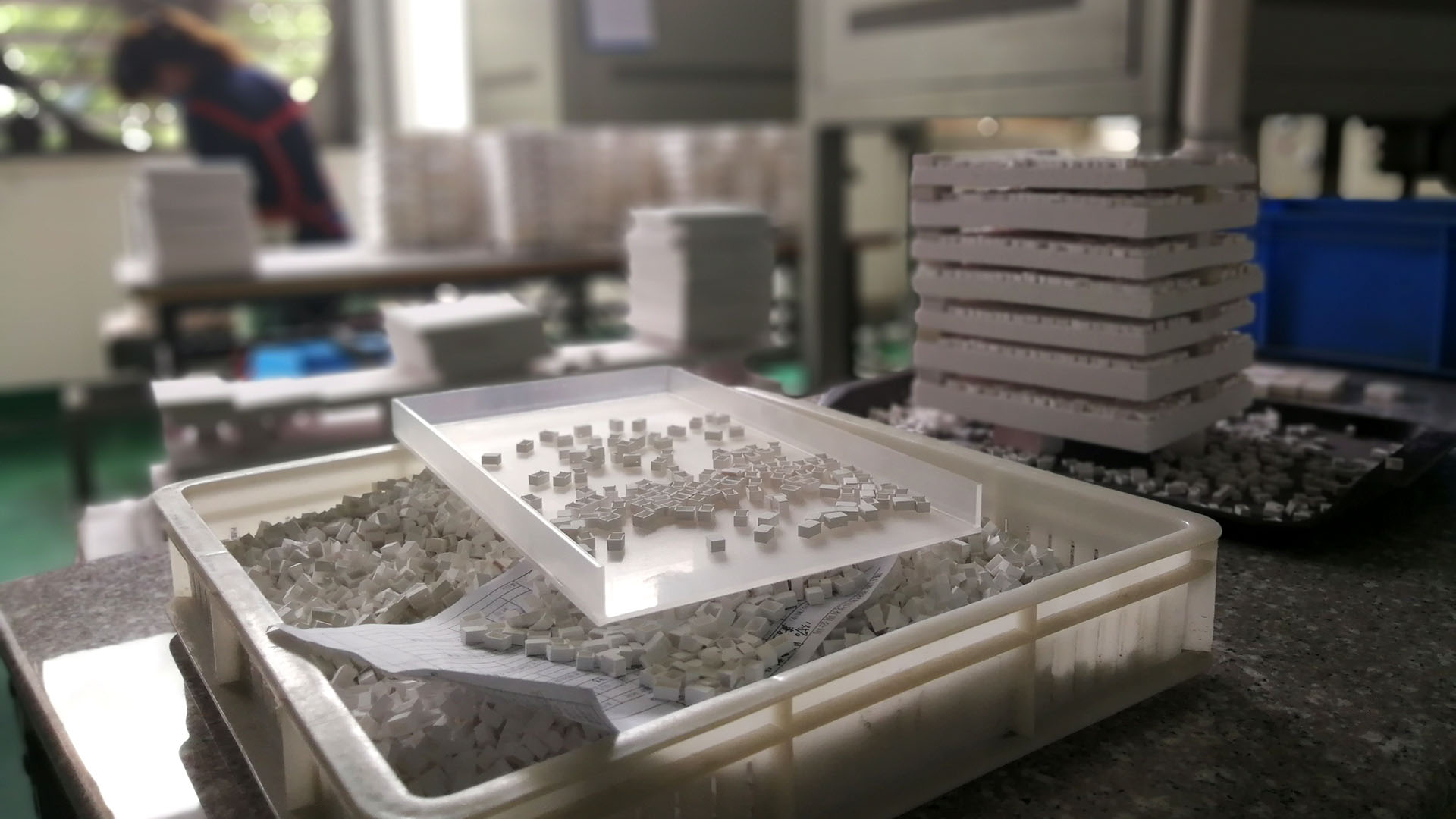
The important processing of advanced ceramic components are produced by sintering (firing) compacted ceramic powder (raw material) forming. The form components are usually referred to as ‘green-state’ and numerous powder-forming processes have been developed including dry pressing, hot pressing, isostatic pressing (CIP and HIP), injection, slip casting and extrusion. However, the powder consists of solid, hard, brittle particulates, so it is difficult to consolidate in a die by pressure alone. A binder is usually added to enhance the flow properties of the powder, leading to higher density in the final component. The binders used vary according to the process to be used and the desired properties of the final product.
Once the ceramic powders have been compacted to produce the green-state component, they are approximately 50-70% dense. They are also relatively weak, but with care can be machined to quite complex geometries. To impart strength, the green state components are usually sintered.
Initial heating (up to 250°C) volatilizes any organic processing additives (binders) and decomposable constituents. As the temperature increases to the firing temperature, consolidation, or sintering of the ceramic powders (solid-state sintering) begins and is usually accompanied by shrinkage. This shrinkage must be accounted (designed) for when machining in the green-state.
Sintering can be assisted (decreasing temperature or time requirements) by the deliberate addition of additives which will react to produce lower melting point green-state been (liquid phase sintering). These secondary phases can be envisaged as “gluing” the ceramic particles together. This is the case for ceramics such as alumina. Sometimes, sintering aids are added to enhance diffusion (which aids sintering), this is the case when additions of boron or aluminum are added to hot-pressed silicon carbide.
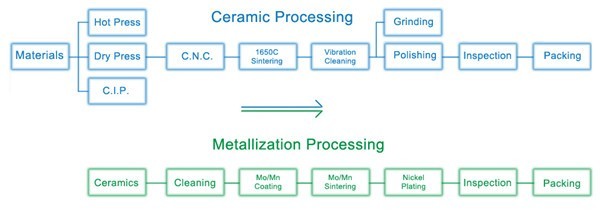
A general flow diagram for ceramic processing is shown as linked.













 Enquiry
Enquiry