Components of modern technology products, such as computer chips or light-emitting diodes, generate more and more waste heat during operation, and generally existing heat dissipation devices used to assist heat dissipation components usually include at least a metal heat sink and a The fan conducts the waste heat from the operation of the heating element through the heat sink to remove it by air convection, and uses the fan to forcibly accelerate the convection of the air around the heating element to achieve the effect of rapid heat removal.
However, the heat transfer coefficient of existing metal heat sinks is not very good. Therefore, heat sinks made of ceramic materials with better heat transfer characteristics appear on the market in order to achieve better heat dissipation effects.
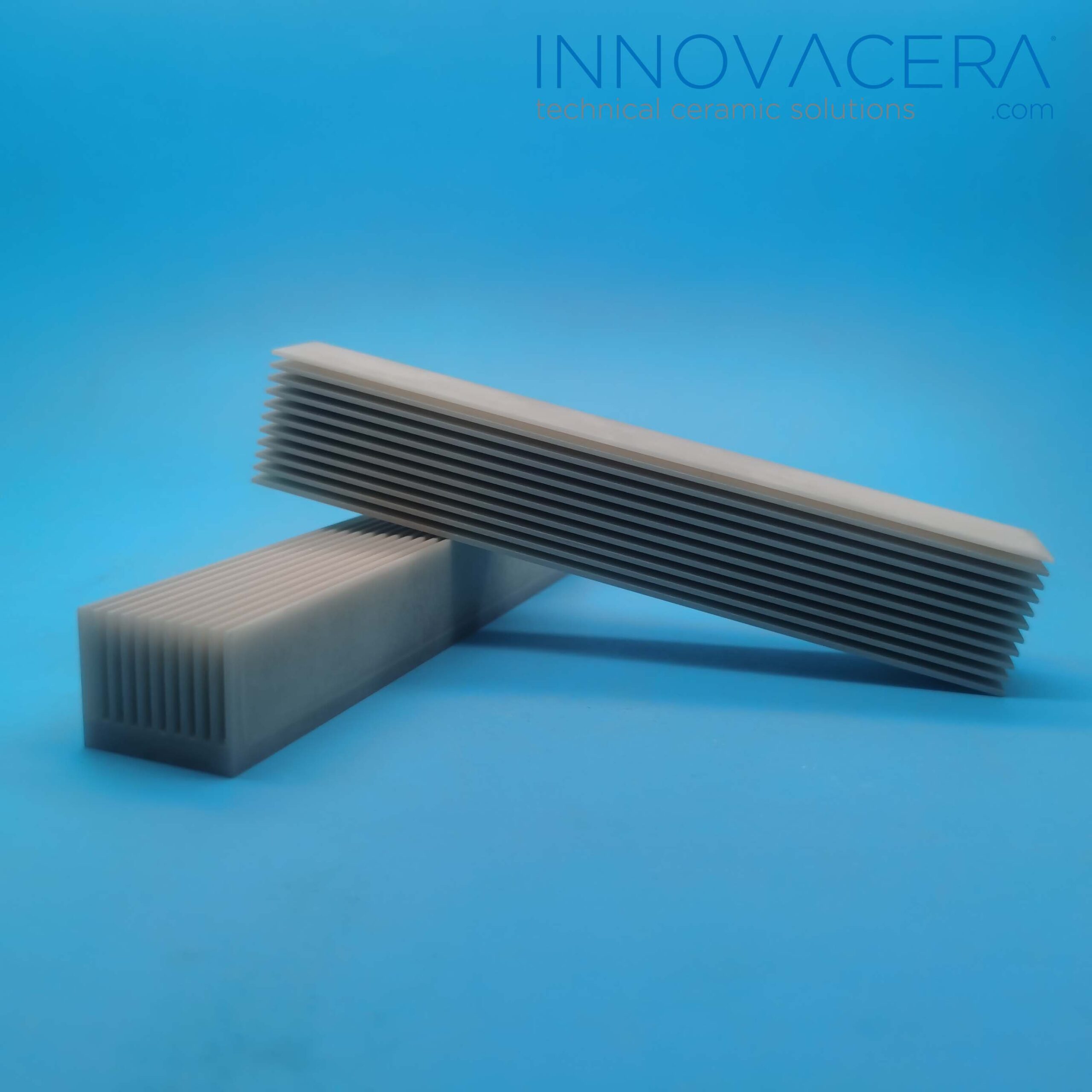
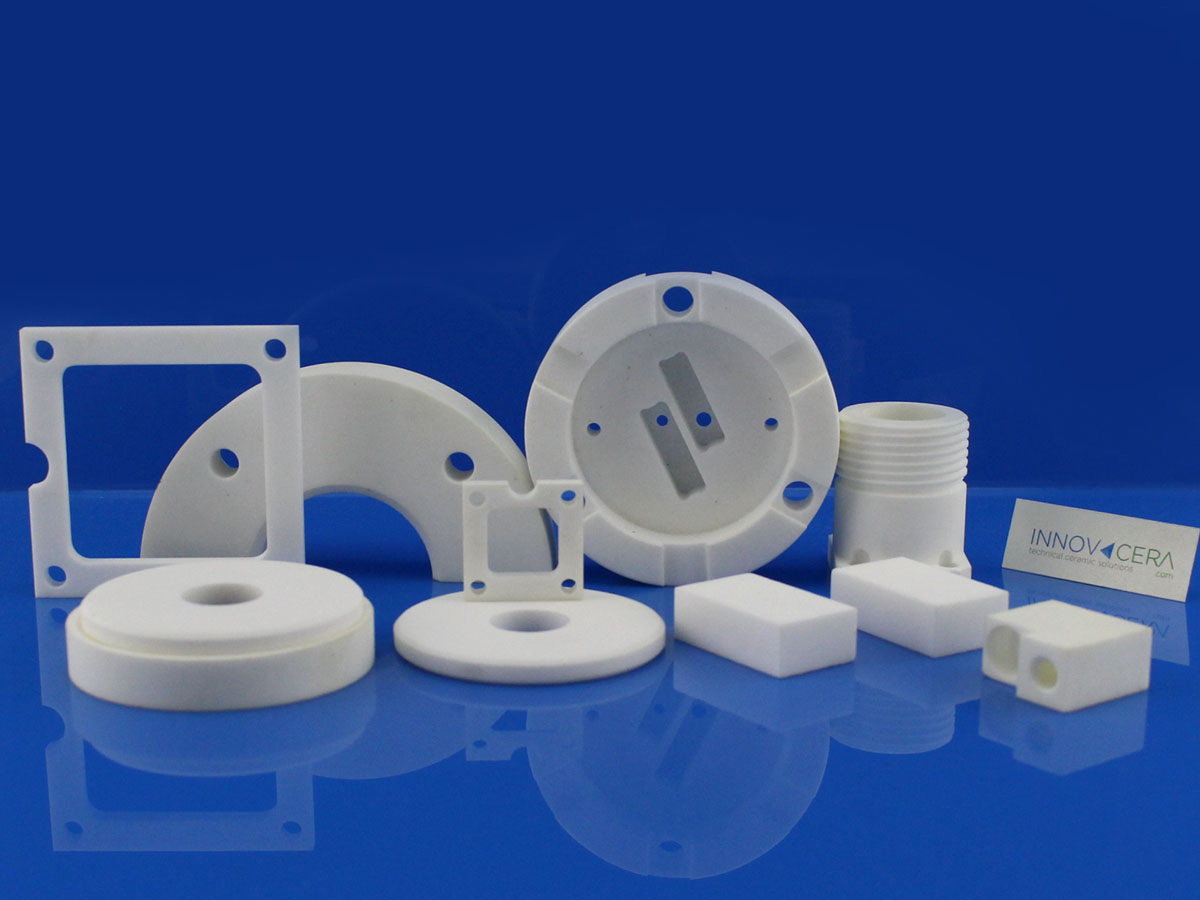
Ceramic heat sink classification
There are aluminum oxide heat sink, aluminum nitride heat sink and silicon carbide heat sink.
There is the performance comparison between usual heatsink VS ceramic
Temperature of Heater itself
(Without heat sink) |
Temperature of heater with heat sinks |
| Usual heatsink |
Ceramic heatsink |
Difference ΔT |
| 150℃ |
90.3℃ |
86.7℃ |
3.6℃ |
| 180℃ |
119.1℃ |
110.8℃ |
8.3℃ |
| 250℃ |
175.4℃ |
164.3℃ |
11.1℃ |
Advantages of Ceramic Heat sink:
1. Do not store heat, and dissipates heat directly, which is fast and reduces the influence of the insulating layer on thermal efficiency;
2. The polycrystalline structure of the ceramic heat sink enhances heat dissipation. Year-on-year conditions, surpassing most thermal insulation materials on the market;
3. The multi-directional heat dissipation of the ceramic heat sink accelerates heat dissipation;
4. High thermal conductivity, high voltage resistance, high temperature resistance, wear resistance, high strength, oxidation resistance, acid and alkali resistance, long service life, and low thermal expansion coefficient, ensuring that it can be used in high and low temperature environments or other harsh environments.
5. Effective in anti-interference (EMI) and anti-static;
6. It is made of natural organic materials, which meets the requirements of environmental protection;
7. Small in size, light in weight, high in strength, saves space, saves materials, saves freight, and is more conducive to the rational layout of product design;
8. Withstand high current, high voltage, prevent leakage and breakdown, has no noise, and will not generate coupling parasitic capacitance with power tubes such as MOS, and thus simplifies the filtering process; the required creepage distance is higher than that of metal bodies The short requirement further saves board space, which is more conducive to the design of engineers and the passing of electrical certification.
Applications:
1. Ceramic heat sinks are mainly used in high-power equipment, IC MOS tubes, IGBT chip-type heat-conducting insulation, high-frequency power supplies, communications, mechanical equipment, high-current, high-voltage, high-temperature and other product components that require heat conduction and heat dissipation insulation.
2. LED lighting, high-frequency welding machine, power amplifier/audio, power transistor, power module, chip IC, inverter, network/broadband, UPS power supply, high-power equipment, etc.













 Enquiry
Enquiry